Figure 2. Ectopic Expression of eIF4A1(F163L) Confers Resistance to Rocaglates in Mammalian Cells.
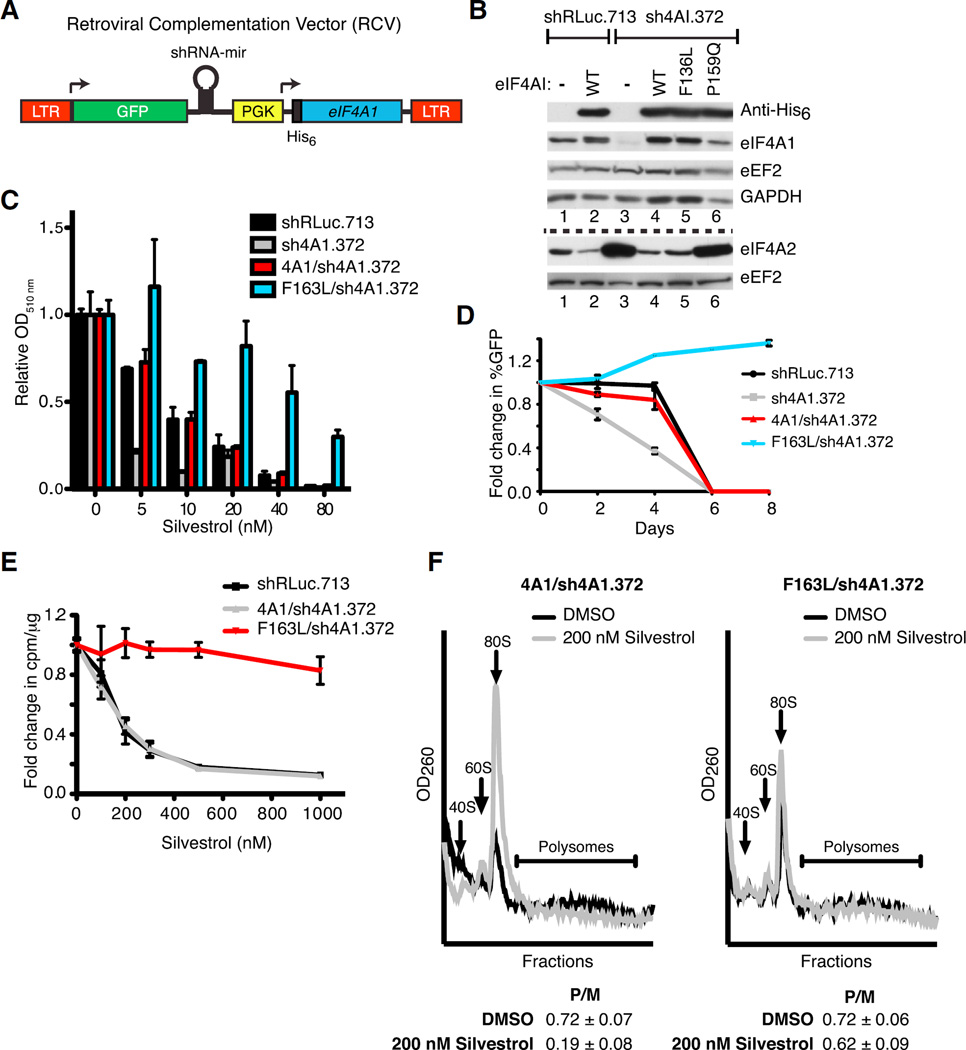
(A) Schematic diagram of RCV designed to simultaneously express an shRNA-resistant His6-eIF4A1 allele while suppressing endogenous eIF4A1.
(B) Representative western blot of NIH/3T3 cells transduced with RCVs. The dashed line separates the two sets of western blots.
(C) Viability assay of RCV-transduced NIH/3T3 cells. Cells were exposed to the indicated concentrations of silvestrol and relative viability was assessed 6 days later by sulforhodamine B (SRB). n = 2 biological replicates performed in duplicates ±SEM.
(D) Competition assay of transduced NIH/3T3 cells. Transduced cells (GFP+) were mixed with parental cells (GFP−) and cultured in the presence of 20 nM silvestrol. The percentage of GFP+ cells was determined on the indicated days. n = 2 biological replicates performed in triplicate ±SEM.
(E) Cells expressing eIF4A1(F163L) are resistant to translation inhibition by silvestrol. Transduced cells were incubated with the indicated concentrations of silvestrol for 1 hr and labeled with [35S]-methionine/cysteine during the last 15 min. n = 4 biological replicates ±SEM.
(F) Polysome profiles of transduced NIH/3T3 cells following exposure to 200 nM silvestrol for 30 min. P/M represents the polysome/monosome ratio. n = 3 biological replicates ±SEM.
See also Figure S1.