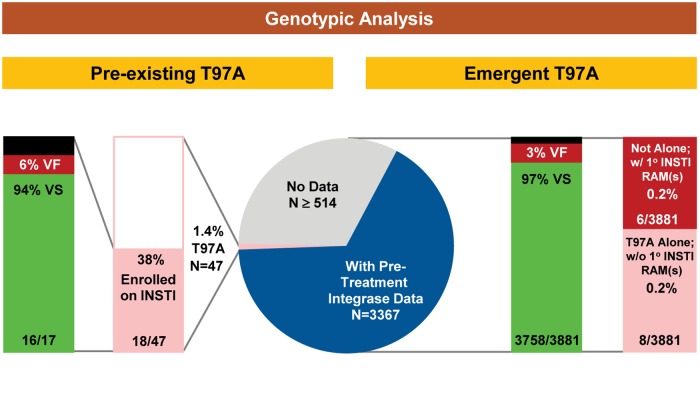
Fig 2. Pre- and on-treatment incidence of HIV-1 infected patients with T97A-based genotypic EVG resistance and impact on treatment outcome.
Grey indicates no data; black indicates excluded data; green indicates virologic success (VS), red indicates virologic failure (VF). Left panel: Forty-seven patients had pre-existing T97A, of which 18 patients (TE = 3; TN = 15) enrolled on an INSTI-based regimen: 16 patients (1 TE [on EVG/r+TDF+DRV] and 15 TN [on EVG/COBI/FTC/TDF]) achieved HIV-1 RNA <50 copies/mL by study endpoint and were considered VS, 1 patient (1 TE [on EVG/r+TDF+DRV]) did not achieve HIV-1 RNA <50 copies/mL by a non-protocol-defined virologic failure visit (Week 8) and was excluded from treatment outcome and study-specific resistance analysis (see Methods), and 1 patient (1 TE [on EVG/r+TDF+DRV]) maintained T97A and EVG sensitivity at confirmed virologic rebound (Week 40) without further development of antiretroviral resistance. Right panel: Eight patients (TE = 7; TN = 1) had emergent T97A alone (ie, in the absence of primary INSTI RAMs): 4 patients at first protocol-defined virologic failure (3 TE [1 on RAL+ABC+LPV/r, 1 on EVG/r+FTC/TDF+LPV, and 1 on EVG/r+MVC+DRV]; 1 TN [on EVG/COBI/FTC/TDF]), 2 patients at second protocol-defined virologic failure (2 TE [1 on EVG/r+TDF+DRV and 1 on RAL+ABC+LPV/r]), 1 patient at fourth protocol-defined virologic failure (1 TE [on EVG/r+TDF+DRV]), and 1 patient (1 TE [on EVG/r+ETR+LPV]) withdrew consent and discontinued study drug at Week 144 and was excluded from treatment outcome and study-specific resistance analysis (see Methods).