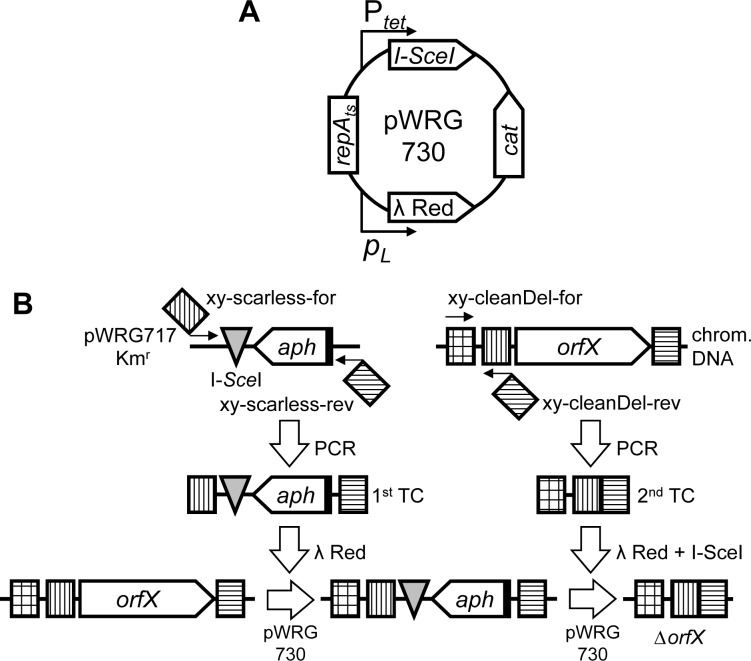
Fig 1. Overview of the method.
(A) Schematic representation of the functional units of plasmid pWRG730. The operon containing λ Red recombinase functions is under control of the heat-inducible phage-derived promoter pL. Expression of the I-SceI meganuclease is controlled by a tetracycline-inducible promoter (Ptet). A chloramphenicol resistance cassette (cat) is used for selection purposes. Due to its temperature-sensitive origin of replication (repAts) the plasmid can be easily cured at elevated growth temperatures. (B) Representation of the two-step scarless deletion methodology. A kanamycin resistance cassette (aph) is amplified together with an I-SceI cleavage site (grey triangle) from pWRG717 with two 60-mer primers each containing site-specific homology extensions at their 5’-ends (striped squares). Chromosomal integration of this first targeting construct (TC) is achieved by λ Red recombinase expression from pWRG730. The 2nd TC is also generated by PCR using chromosomal DNA as template and contains a direct fusion of up- and downstream homology regions. After genomic integration of the 2nd TC using λ Red recombinase, successful recombinants are selected by I-SceI expression from pWRG730. A detailed description of the method can be found in the main text.