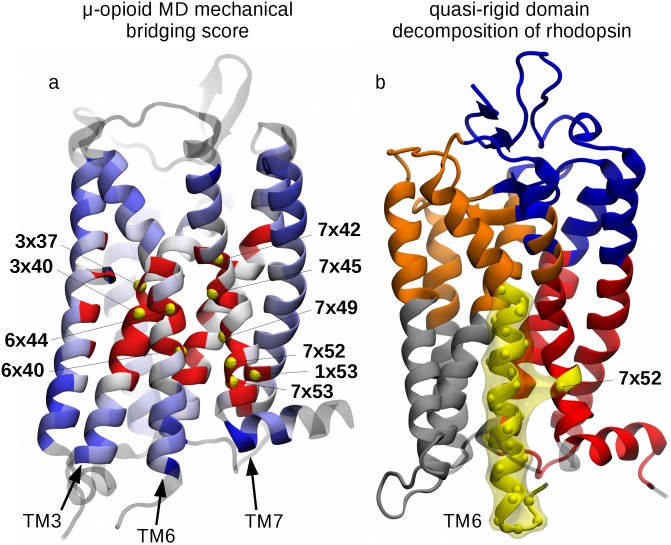
Fig 4. Functional role of site 7x52: MD simulations and quasi-rigid domain decomposition.
(a) Amino acids of the μ-opioid receptor (PDB ID: 4DKL) are color-coded according to the mechanical bridging score computed from atomistic molecular dynamics simulations. The color convention is the same as in Fig 2, with the top 10 ranking residues being labelled and highlighted with yellow beads, corresponding to the following sites, in decreasing order of score: 6x40, 7x52, 7x45, 3x40, 1x53, 7x49, 7x42, 7x53, 3x37, 6x44 (in boldface, the key functional sites also present in the list of Tehan et al. [23]). Panel (b) shows the optimal SPECTRUS [19] decomposition of rhodopsin into 5 quasi-rigid domains. The TM6-based domain is highlighted in yellow and it notably includes residue 7x52 from TM7. Analogous decompositions for the other receptors are shown in Fig I in S1 Supporting Information.