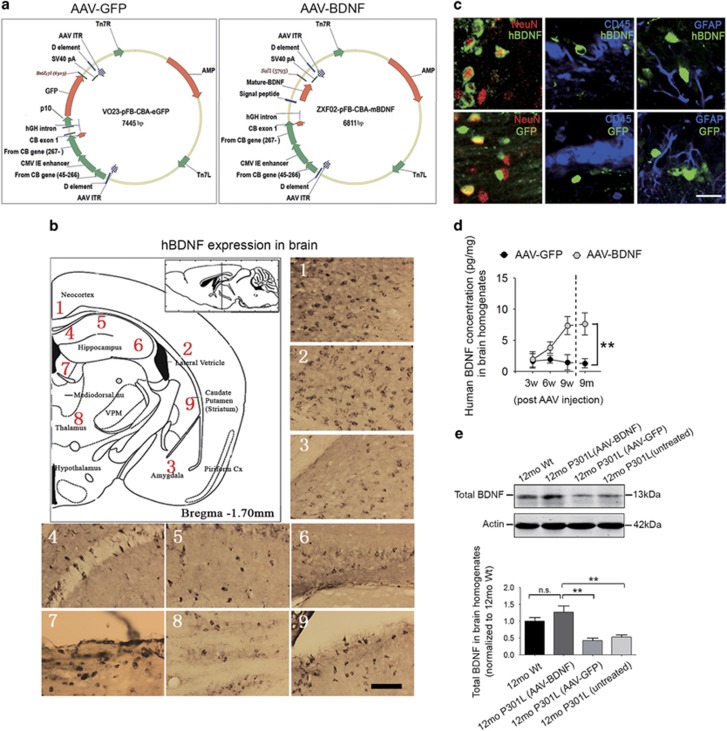
Figure 2.
Wide and stable expression of human brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) after intraventricular injection of adeno-associated virus carrying BDNF (AAV-BDNF). (a) Schematics of the construction and characterization of AAV-green fluorescent protein (AAV-GFP; left panel) and AAV-BDNF (right panel) vectors. (b, c) In order to exclude endogenous mouse BDNF, we applied a specific anti-human BDNF antibody to detect the expression of human BDNF within P301L mouse brain. Human BDNF expression is detectable in multiple brain regions (b), and GFP or human BDNF was selectively expressed in neurons but not in microglia (CD45-positive) or astrocytes (glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP)-positive) (c). Scale bar=80μm (b) or 40μm (c). (d) Comparison of human BDNF levels in brain homogenates of P301L mice treated with AAV-BDNF or AAV-GFP at 3 weeks (3w), 6 weeks (6w), 9 weeks (9w) and 9 months (9 m) after AAV injection initiated at 3 months of age (n=4 per group for 3w, 6w and 9w; n=6 for 9 m group; mean±s.e.m.; two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA), Tukey's test, **P<0.01). The concentrations of human BDNF were determined using specific human BDNF enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kits. (e) Western analysis of total BDNF expression (including endogenous mouse BDNF and exogenous human BDNF) in brain homogenates (n=5 per group; mean±s.e.m., one-way ANOVA, Tukey's test, **P<0.05; n.s. denotes no significant difference). 12mo P301L (AAV-BDNF) and 12mo P301L (AAV-GFP) denote 12-month-old P301L mice treated with AAV-BDNF and AAV-GFP, respectively; 12mo P301L (untreated) denotes untreated 12-month-old P301L mice; 12mo Wt denotes age-matched wild-type littermates.