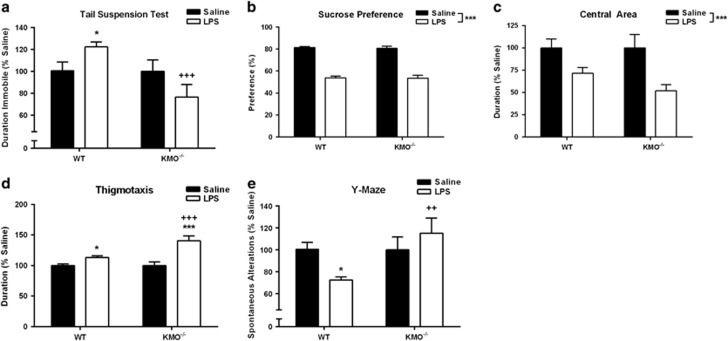
Figure 3.
Kynurenine 3-monooxygenase (KMO) knockout mice are protected from distinct inflammation-induced depressive-like behaviors. (a) Twenty-four hours following injection with either lipopolysaccharide (LPS) or saline, wild type (WT) and KMO−/− mice were tested in the tail suspension test (TST) to assess behavioral despair. LPS increases duration spent immobile (seconds, represented as % Saline) in WT mice but not in KMO−/− mice. (b) Sucrose and water intake were recorded for the 24h following LPS or saline injections and were used to calculate sucrose preference (SP) to assess anhedonia-like behavior. LPS treatment resulted in a characteristic reduction in SP in both WT and KMO−/− mice. (c) Similarly, at 24 h post treatment, duration (seconds, represented as % Saline) in the center of the open field (OF) was recorded as an index of anxiety-like behavior. (d) Duration spent near the walls of the OF or thigmotaxis behavior (seconds, represented as % Saline) was also recorded to asses anxiety-like behavior. In both OF assessments (c, d), LPS treatment resulted in similar elevations in anxiety-like behavior in WT and KMO−/− mice. (e) Spontaneous alterations (represented as % Saline) between the three arms of a Y-maze were recorded as an index of working memory. LPS treatment resulted in a significant deficit in spontaneous alterations in WT mice but KMO−/− mice were unaffected. Data represent sample means ± s.e.m. n=13–29 mice per group. *Main effect or post hoc comparison between saline and LPS within the same genotype. +Post hoc comparison to WT with the same intraperitoneal (i.p.) treatment. *,+P<0.05–0.01; **,++P<0.01–0.001; ***,+++P<0.001.