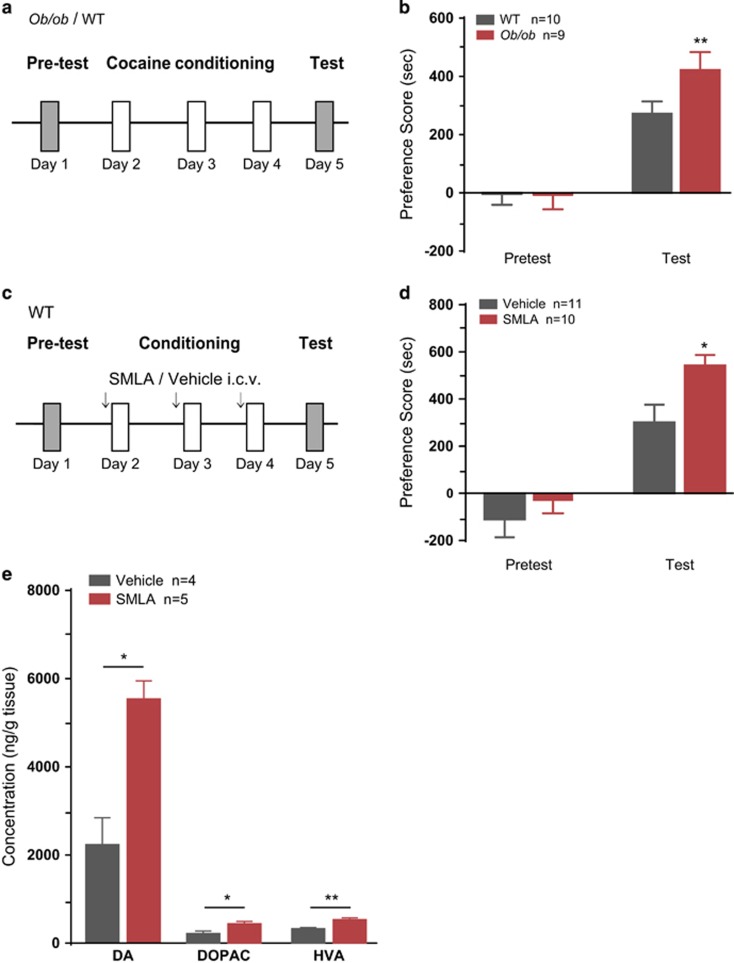
Figure 1.
Downregulation of leptin signaling increases cocaine-CPP and dopamine levels in the NAc. (a) Schematic of the cocaine-CPP experimental schedule. WT and Ob/ob mice were tested for place preference on Day 1 and received cocaine (15 mg kg−1, i.p.) conditioning on Days 2, 3 and 4. On Day 5, mice were allowed to freely explore the entire apparatus for 20 min, and the time spent in each chamber was recorded. (b) Quantification of the place preference scores of WT and Ob/ob mice in the pre-test and test sessions. (c) Schematic of the experimental schedule. WT mice received an infusion of ACSF or SMLA (500 ng, i.c.v.) 30 min before conditioning sessions. (d) Quantification of the place preference scores in the pre-test and test sessions. (e) Concentrations of cocaine-induced monoamine neurotransmitters including DA, DOPAC and HVA in the NAc of mice receiving SMLA or Vehicle i.c.v. infusion 30 min before the cocaine injection were detected by HPLC. The data are presented as the mean±s.e.m. *P<0.05, **P<0.01. ACSF, artificial cerebrospinal fluid; CPP, conditioned preference place; HPLC, high-performance liquid chromatography; i.c.v., intracerebroventricular; NAc, nucleus accumbens; SMLA, superactive mouse leptin antagonist; WT, wild-type.