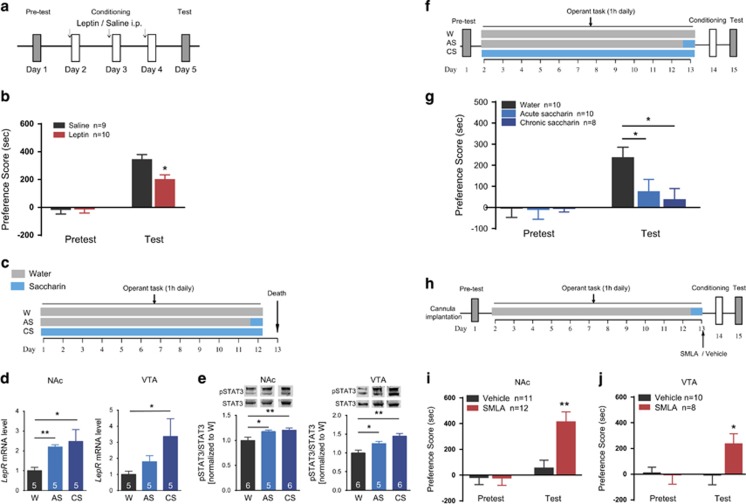
Figure 5.
Upregulated leptin signaling reduces cocaine-CPP. (a, b) Mice received injection of saline or leptin (1 mg kg−1 i.p.) 30 min before conditioning, and the quantification of the place preference scores in the pre-test and test sessions is shown. (c) Schematic of the saccharin reward experimental schedule. Three groups of mice were confined to the apparatus for a 1-h operant task for 12 days to receive water (W) or saccharin daily (CS) or saccharin only on the last session (AS). The mice were decapitated 24 h after the last session. (d, e) The levels of LepR mRNA (d), pSTAT3 protein and total STAT3 (e) in the NAc and VTA were detected. Images are representative of similar results from five to six independent individuals. (f) Schematic of the operant task and cocaine-CPP schedule. Three groups of mice (W, AS and CS) performed a 1 h operant task for 12 days, and 24 h after the last session, each mouse received cocaine-context conditioning learning. Place preference was examined 24 h later. (g) Quantification of the place preference scores of the three groups of mice in the pre-test and test sessions. (h) Schematic of the modified cocaine-CPP schedule. SMLA (500 ng) or vehicle was infused into the NAc or VTA 30 min after saccharin administration, and the mice received cocaine-context conditioning 24 h later. (i, j) Quantification of the place preference scores of mice receiving SMLA (500 ng) infusion into the NAc (i) or VTA (j) after saccharin administration in the pre-test and test sessions. The data are presented as the mean±s.e.m. *P<0.05, **P<0.01. CPP, conditioned place preference; NAc, nucleus accumbens; SMLA, superactive mouse leptin antagonist; VTA, ventral tegmental area.