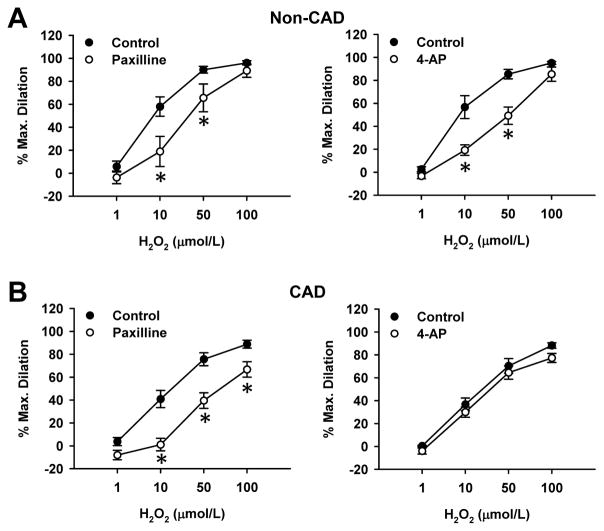
Figure 1. Role of BKCa and KV channels in H2O2-induced dilation of human adipose arterioles from non-CAD and CAD subjects.
H2O2 induced dose-dependent dilation in adipose arterioles. The dilation was reduced by paxilline (100 nmol/L), a BKCa channel blocker, in both non-CAD (A, left) and CAD (B, left) arterioles. In contrast, 4-AP (10 mmol/L), a general KV channel blocker, reduced the dilation in non-CAD (A, right) but not CAD (B, right) arterioles, suggesting a loss of KV channel function in disease. *P<0.05 versus control; n=5–6 vessels/group.