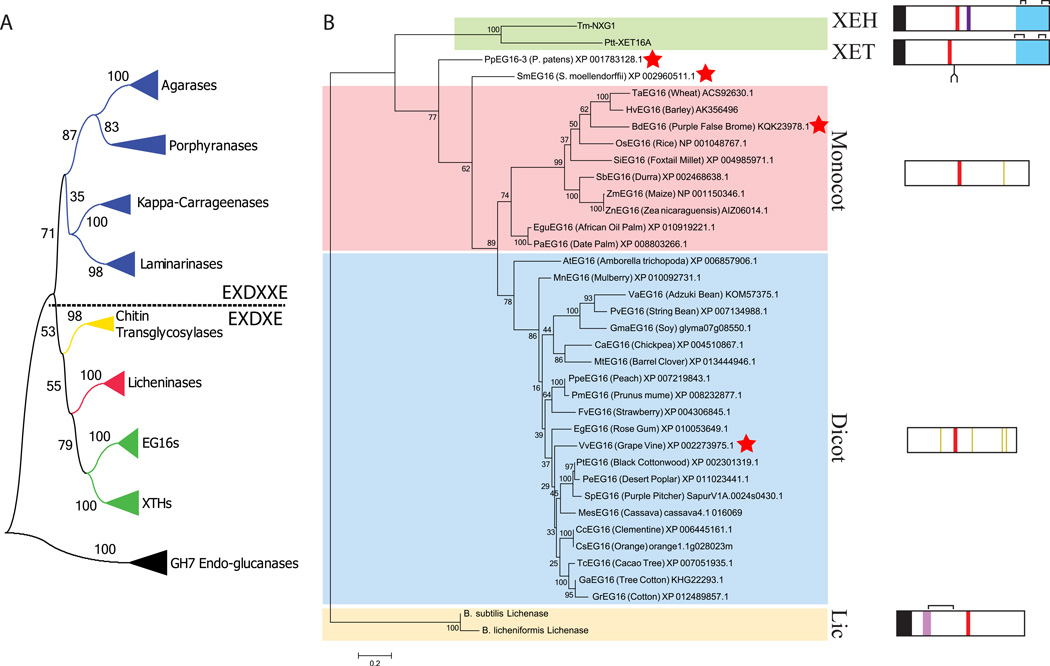
Figure 1.
Protein sequence-based phylogeny EG16 homologs within Glycoside Hydrolase Family 16 (GH16). A) Overall phylogeny of GH16 encompassing all specificities identified to date. Each collapsed branch represents 5 sequences (Table S5). The tree is rooted with 5 GH7 cellulases; GH7 and GH16 together form Clan GH-B. A dashed line separates enzymes containing the EXDXXE “beta-bulge” active-site motif from those with the regular beta-strand EXDXE active-site motif. B) Phylogenetic tree of EG16 homologs identified in Genbank and Phytozome, based on the protein sequence alignment shown in Figure S1. Abbreviated protein names are derived from the genus and species of origin (see corresponding GenBank entries); the common name (where available) is given along with the accession code. The tree is rooted using two Bacillus licheninases and additionally includes a xyloglucan endo-transglycosylase (PttXET16A, (Johansson, et al. 2004)) and a xyloglucan endo-hydrolase (TmNXG1, (Baumann, et al. 2007)) as outliers with known tertiary structures. Sequences indicated with a red star were selected for recombinant expression in E. coli (Table S1). Box diagrams, to scale, indicate key protein sequence features: Black, signal peptides; red, active site EXDXE motif; light purple, licheninase loop extension; dark purple, XEH loop extension; blue, C-terminal XET/XEH extension (XET_C); yellow, conserved cysteine residues in the monocot or dicot EG16 clades; brackets, crystallographically observed disulfide bonds; fork, conserved XET N-glycosylation site. Bootstrap values from 100 maximum likelihood resamplings are shown next to each branch of both trees.