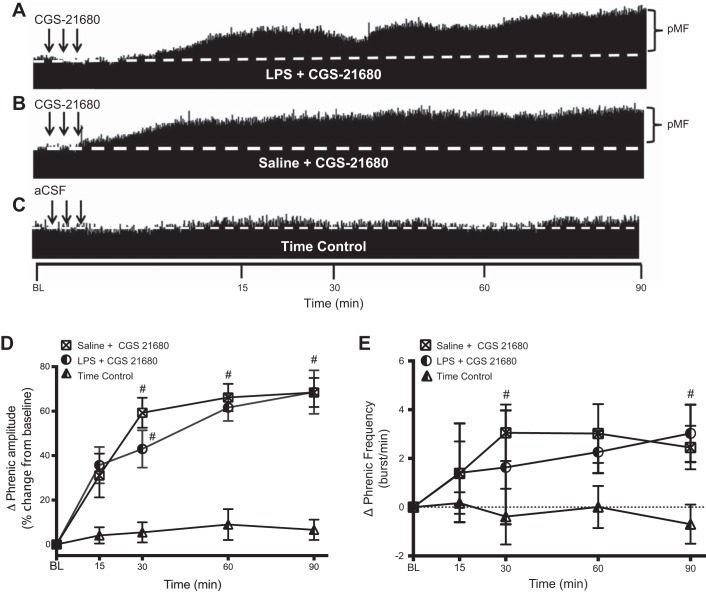
Fig. 5.
A2A receptor agonist-induced pMF is unaffected by LPS. A–C: representative traces of compressed integrated phrenic neurograms following intrathecal CGS-21680. A: LPS treatment and intrathecal CGS-21680 shows increases in burst amplitude vs. BL. B: saline treatment and intrathecal CGS-21680 shows increased amplitude vs. BL. C: the time control group given intrathecal vehicle, aCSF, did not show any time-dependent increase in phrenic burst amplitude. D: group data for phrenic amplitude as a %change from BL. LPS + CGS-21680 (circles; n = 6) and saline + CGS-21680 (squares; n = 6) are compared with aCSF-treated rats (triangle; n = 10). After intrathecal CGS-21680, pMF persisted at least 90 min. There was a significant difference from time control (#P < 0.05) for LPS + CGS-21680 and saline + CGS-21680 vs. aCSF at 30, 60, and 90 min. There was no significant difference between LPS + CGS-21680 and saline + CGS-21680 at any time. E: group data for phrenic burst frequency (bursts/min). LPS + CGS-21680 and saline + CGS-21680 are compared with aCSF (time control) protocols. The LPS + CGS-21680 group was significantly different from time control (#P < 0.05) at 90 min. The saline + CGS-21680 group was significantly different from time Control (#P < 0.05) at 30 min.