Fig. 3a–d.
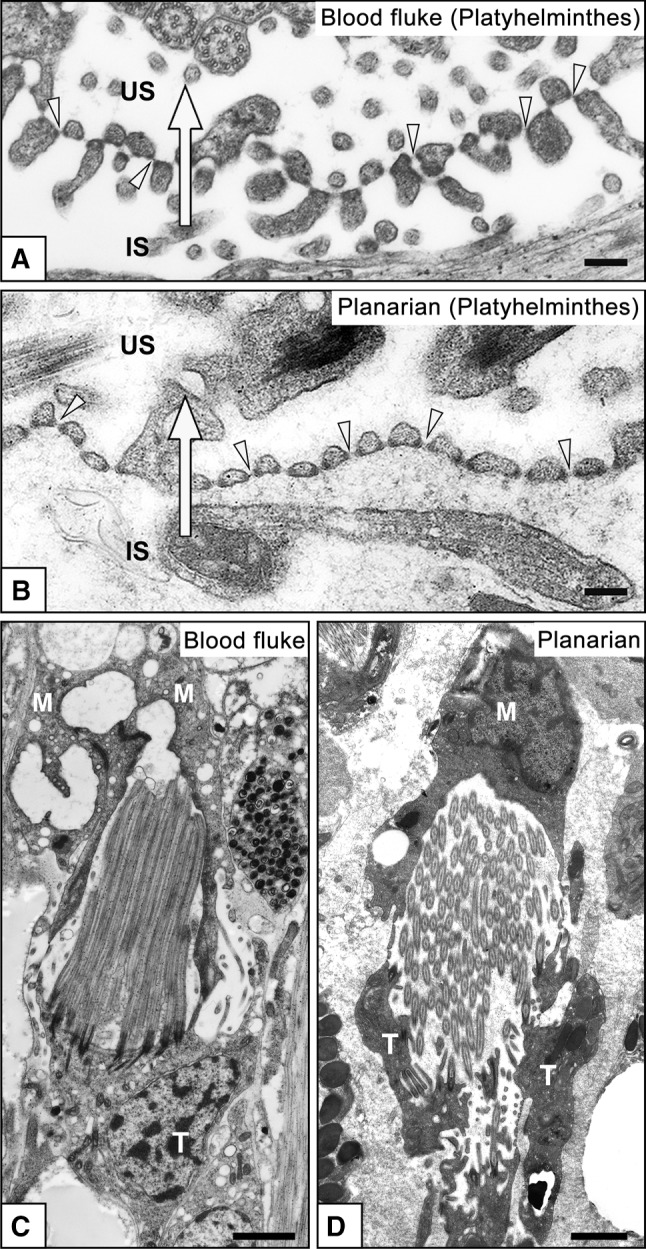
Terminal cells in Platyhelminthes. Transmission electron micrographs of terminal cells in the blood fluke Schistosoma mansoni (a, c), and freshwater planarian Dugesia japonica (b, d). Terminal cells form filtration slits for ultrafiltration, which are spanned by membranous structures, the slit diaphragms (arrowheads in a, b). The attachment sites of slit diaphragms are associated with electron-dense plaques. The terminal cell is interdigitated with a modulating tubular epithelial cell to form filtration slits in the blood fluke (as shown in Fig. 2b). In the planarian, formation of the filtration slits remains unclear. Several dozen motile cilia protrude from the luminal surface of the terminal cell (c, d). IS Interstitial space, M epithelial cell of modulating tubule, T terminal cell, US urinary space (lumen of protonephridium). Arrows Direction of primary urine flow. Bars a, b 200 nm; c, d 5 μm
