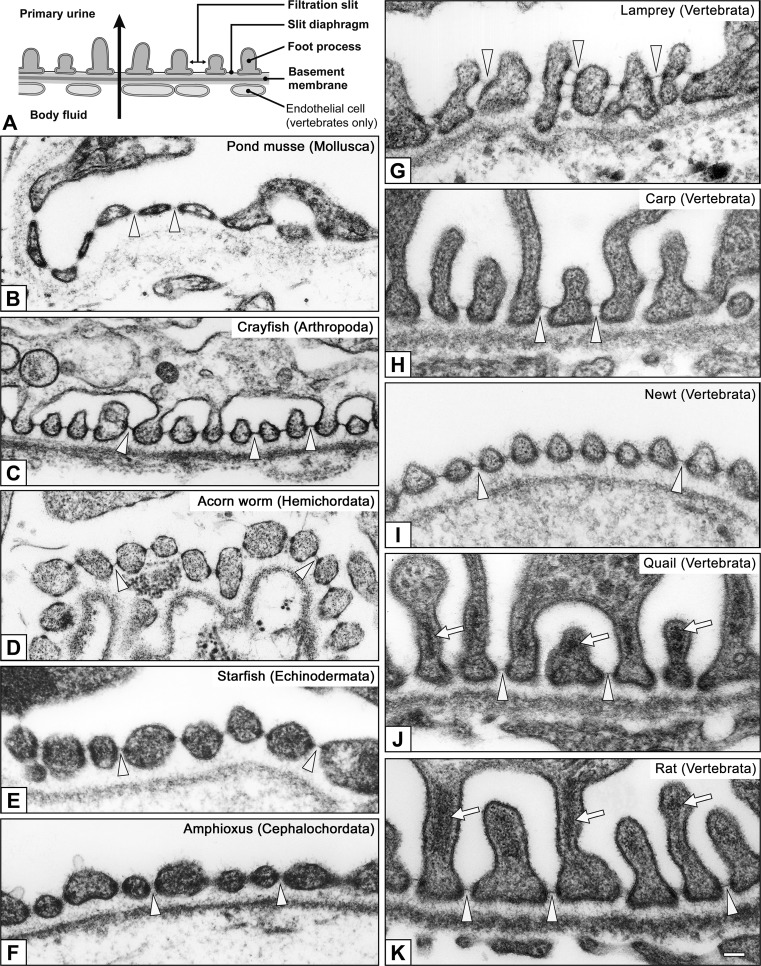
Fig. 4a–k.
Foot processes and slit diaphragms in podocytes. Basic structure of the metanephridial podocytes is conserved among eucoelomates. The filtration site consists of the foot processes, slit diaphragms, and basement membrane (a); the foot processes widely vary in shape and size among invertebrates (b–f) and vertebrates (g–k). The foot processes contain prominent actin bundles only in quail and rat podocytes (arrows in j, k). Actin bundles contribute to the mechanical protection of the glomerular wall from higher glomerular capillary pressure peculiar to birds and mammals. In vertebrates, glomerular endothelial cells are also contained in the filtration barrier. b Pond mussel (Sinanodonta lauta), c Crayfish (Procambarus clarkii), d Acorn worm (Balanoglossus misakiensis), e Starfish (Patiria pectinifera), f Amphioxus (Branchiostoma japonicum), g Lamprey (Lampetra japonica), h Carp (Cyprinus carpio), i Newt (Cynops pyrrhogaster), j Quail (Coturnix japonica), k Rat (Rattus norvegicus). Arrowheads slit diaphragm. Bar 200 nm