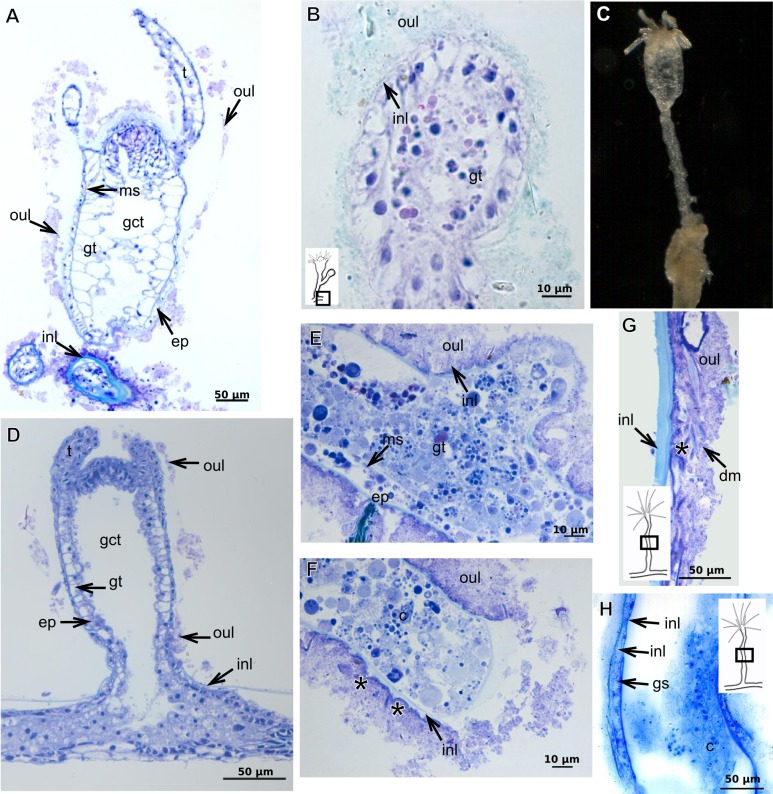
Figure 21. Development of the exoskeleton.
(A)–(C) Bimeria vestita Wright, 1859. (A) Developing polyp in culture with filtered water of, stained with TB; (B) developing stolon, stained with AB + PAS + H; (C) external view of a polyp in culture with unfiltered water; (D)–(F) Bougainvillia muscus (Allman, 1863). (D)–(F) Stained with TB; (D) developing stolonal hydranth; (E) stolon of developing hydranth; (F) development of stolon of the hydrorhiza; (G)–(H) Parawrightia robusta Warren, 1907. (G) Hydrocauline exoskeleton of specimens maintained in culture conditions (unfiltered water), stained with AB; (H) hydrocauline exoskeleton of specimens maintained in culture conditions (unfiltered water), stained with HgBpB. Asterisk indicates “perisarc extensions.” Abbreviations: dm, diatoms; ep, epidermis; gct, gastrovascular cavity; gs, secretory granules; gt, gastrodermis; inl, inner layer; ms, mesoglea; oul, outer layer.