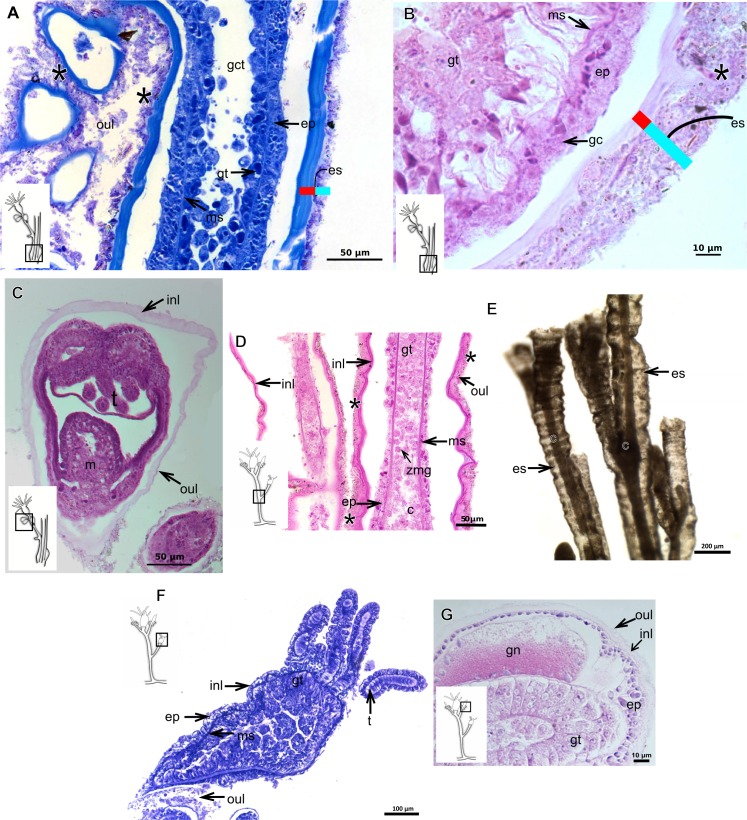
Figure 7. Exoskeletal structure.
(A)–(C) Bougainvillia sp. (A) detail of hydrocauline exoskeleton, stained with TB; (B)–(C) stained with PAS; (B) transverse section of hydrocauline exoskeleton; (C) gonophore with complete medusa with manubrium and marginal tentacle linked to the bulb. (D)–(G) Dicoryne conferta Alder, 1856. (D) hydrocaulus of the central region of the polyp, stained with PAS; (E) external appearance of the exoskeleton; (F) exoskeleton of the hydranth, stained with TB; (G) mature female gonophore with sporosacs of styloid type, stained with HE. Cyan-blue line indicates the outer layer of the exoskeleton (=exosarc), red line indicates the inner layer of the exoskeleton (=perisarc), asterisk indicates “perisarc extensions.” Abbreviations: c, coenosarc; ep, epidermis; es, exoskeleton; gn, gonadal cell cluster; gt, gastrodermis; inl, inner layer; m, manubrium; ms, mesoglea; oul, outer layer; t, tentacle.