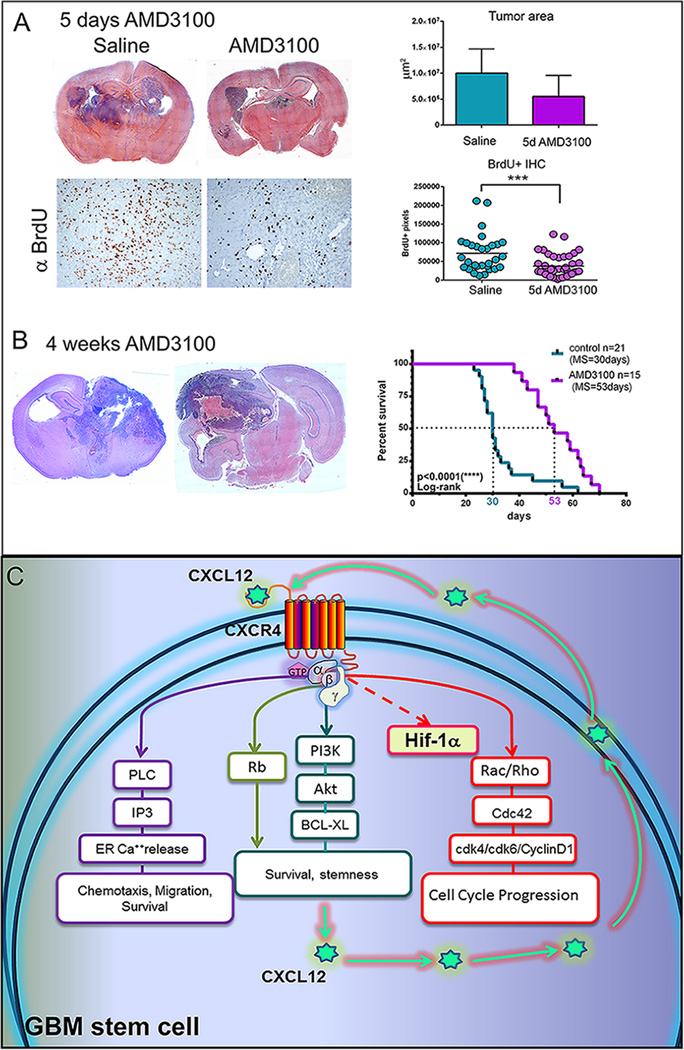
Figure 6. A. Treatment of tumor-bearing mice with AMD3100 increases their survival and decreases cell cycle progression of tumor cells.
Upper panel illustrates hematoxylin and eosin stained coronal brain sections from animals treated for 5days with saline or AMD3100 and quantitation of tumor areas (S7) at their largest diameter (n=4 per group). Lower panel are representative micrographs of immunohistochemistry detecting BrdU and quantitation of BrdU uptake in the tumors from animals treated with saline or AMD3100 (10 images per animal taken at 20× magnification). Unpaired, two-tailed t-test was performed with GraphPad Prism (***p<0.001). B. Treatment with AMD3100 increases survival of animals bearing tumors induced with NRAS and SV40LgT.To the left are representative coronal sections stained with hematoxylin and eosin from brains of moribund animals treated or not with AMD3100. Presented to the right is the survival curve comparing the median survival (MS=53 days) of 15 animals treated with AMD3100 osmotic pumps with the survival of 63 untreated controls (MS=30 days). Median survival was compared using the Log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test shows significant difference (p<0.0001, ****). C. Schematic representation of the proposed mechanism of action of the CXCL12/CXCR4 signaling axis. CXCL12 produced by the tumor cells acts upon the GPCR receptor CXCR4 to activate multiple pathways. Activation of PI3K leads to the increase in pAkt and BCL-XL promoting survival and stemness. Activation of the Phopspholipase C also leads to release of Calcium from intracellular stores and triggers chemotaxis and migration and promotes survival. Activation of the Rho family of GTPases Rac/Rho and Cdc42 leads to microtubule reorganization, increased transcription and translation of Cyclin D1, CDK4 and CDK6 and to cell cycle progression. Under hypoxic conditionsCXCL12 may induce the expression of HIF-1α.