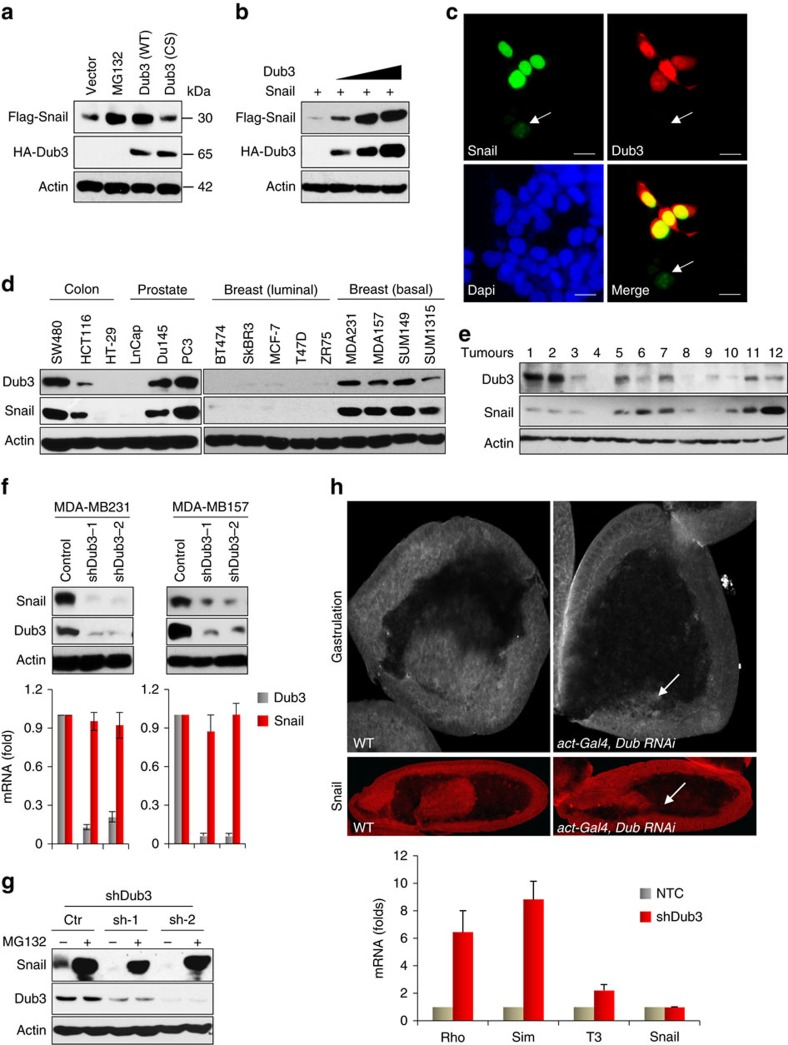
Figure 1. Dub3 stabilizes Snail1.
(a) Flag-Snail1 was co-expressed with HA-tagged Dub3 (either wild-type, WT, or catalytic inactive C89S mutant, CS) in HEK293 cells or cells were treated with MG132 for 6 h. Expression of Snail1 and Dub3 were assessed by western blot. (b) Flag-Snail1 was co-expressed with increasing amounts of HA-Dub3 in HEK293 cells. Lysates were subjected to analysis by western blot. (c) GFP-Snail1 was co-expressed with HA-Dub3 in HEK293 cells. After fixation, the cellular location of Snail1 (green) and Dub3 (red) was examined by immunofluorescent (IF) staining using anti-HA antibody and visualized by fluorescence microscopy (nuclei were stained with Dapi; blue). Arrowhead identifies a cell expressing only GFP-Snail1 but not Dub3. Scale bars, 25 μm. (d) The protein expression of Dub3 and Snail1 in various cancer cell lines was analysed by western blot. (e) Expression of Dub3 and Snail1 from 12 human breast tumours (fresh frozen) was analysed by western blot. (f) The protein expression of Dub3 and Snail1 from MDA-MB157 and MDA-MB231 cells stably transfected with control or two individual Dub3 shRNAs was analysed by western blot and the mRNA was detected by real-time PCR (mean±s.e.m. in three separate experiments). (g) The protein expression of Dub3 and Snail1 from MDA-MB157 cells stably transfected with control or two individual Dub3 shRNAs and treated with or without 10 μM MG132 for 6 h was analysed by western blot. (h) Gastrulation and Snail1 expression were detected in Drosophila embryos and the mRNA was detected by real-time PCR using stage 11 cells (mean±s.e.m. in three separate experiments).