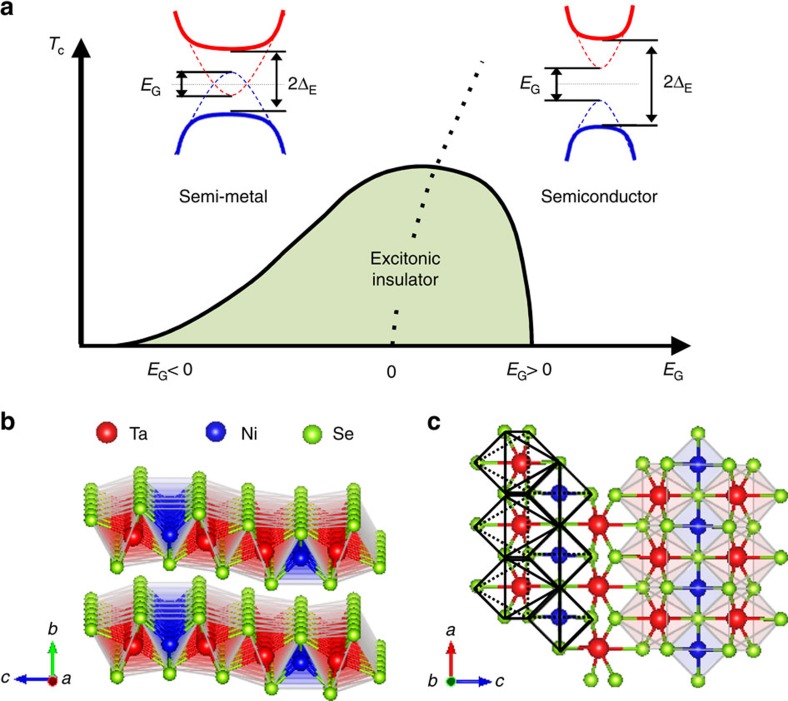
Figure 1. Excitonic insulator and Ta2NiSe5 structure.
(a) Schematic phase diagram of excitonic gap formation as a function of EG. The dotted line indicates the crossover from semimetallic to semiconducting behaviour. The insets show the relation between EG and ΔE for the metallic and insulating limits. EG is the one-electron bandgap between conduction (red) and valence band (blue). The Coulomb interaction between electron- and hole-like excitations can lead to electron–hole pairing (exciton formation) and the opening of a new many-body excitation gap ΔE in the excitonic insulator phase. (b) The orthorhombic phase of Ta2NiSe5 shown in two orientations emphasizing the layered nature in the a–c plane, and (c) the TaSe6 and NiSe4 chains along the a direction (right).