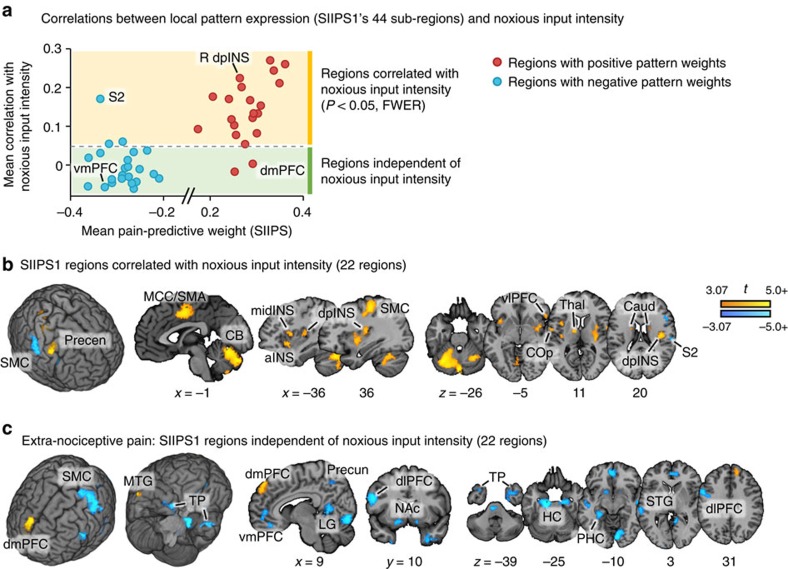
Figure 2. Deconstructing the SIIPS1.
(a) Each dot of the scatter plots represents a contiguous brain region from the SIIPS1 thresholded at q<0.05, FDR corrected (see Fig. 1c). Red dots represent regions with positive predictive weights, and blue dots represent regions with negative predictive weights. The y axis of the scatter plots shows the mean correlations between the local pattern expression (with absolute pattern weights) and trial-by-trial noxious stimulus intensity across 183 participants from Studies 1–6. The x axis of the scatter plots shows the mean pattern weights of contiguous regions. Dashed gray lines indicate one-sample t-test results that are corrected for multiple comparisons using family-wise error rate<0.05 (Bonferroni methods; equivalent to uncorrected P<0.0011). Therefore, dots above the dashed lines indicate regions significantly correlated with noxious input intensity (temperature) and dots below the dashed line indicate regions independent of noxious input intensity. Brain region maps for (b) regions that showed significant non-zero correlations with noxious input intensity and for (c) regions that showed no correlations with noxious input intensity, but still contributed to the prediction of single-trial level pain ratings. Region labels, mean weight values and mean correlation values with noxious stimulus intensity (and their t- and p-values) can be found in Supplementary Table 4. aINS, anterior insula; Caud, caudate; CB, cerebellum; dmPFC, dorsomedial PFC; dlPFC, dorso-lateral PFC; dpINS, dorsal posterior insula; HC, hippocampal area; LG, lingual gyrus; MCC, middle cingulate cortex; midINS, middle insula; MTG, middle temporal gyrus; NAc, nucleus accumbens; PHC, parahippocampal area; Precen, precentral cortex; Precun, precuneus; S2, secondary somatosensory cortex; SMA, supplementary motor area; SMC, sensory motor cortex; STG, superior temporal gyrus; Thal, thalamus; TP, temporal pole; vlPFC, ventrolateral PFC; vmPFC, ventro-medial PFC.