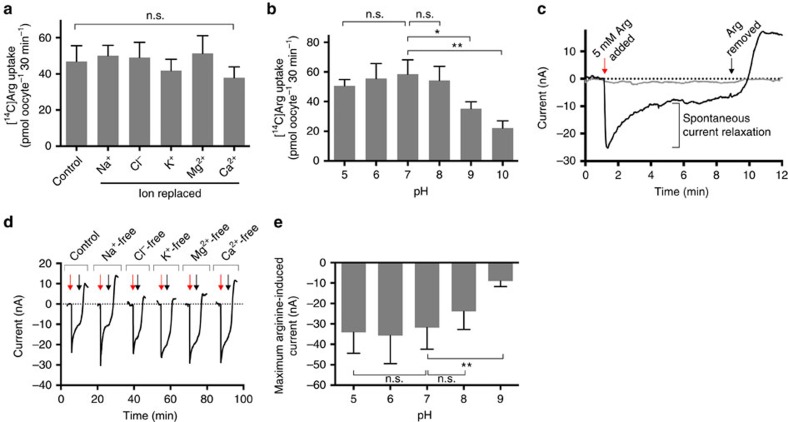
Figure 4. Characteristics of arginine transport by TgNPT1.
(a,b) Ion-dependence (a) and pH-dependence (b) of TgNPT1-mediated arginine transport in oocytes expressing TgNPT1-HA. The uptake of 0.4 μCi ml−1 (1.1 μM) [14C]Arg was measured in the presence of 100 μM unlabelled arginine in oocytes, in either complete ND96 uptake buffer (control), media in which Na+, Cl−, K+, Mg2+, or Ca2+ ions were replaced (a), or media pH-adjusted to pH 5–10 (b). Uptake measured in uninjected control oocytes was subtracted from that measured in TgNPT1-HA-expressing oocytes to yield the TgNPT1-mediated uptake. All data were averaged from three independent experiments, each conducted on oocytes from a different frog (*P<0.05, **P<0.01; n.s.=not significant; ANOVA). (c) A representative trace for the arginine-induced current in a TgNPT1-HA-expressing oocyte (black) and an uninjected oocyte (grey). The red arrow indicates the point of addition of 5 mM arginine to the ND96 medium and the black arrow indicates the point at which arginine was removed. The spontaneous current relaxation following the addition of 5 mM arginine is indicated. (d) Representative traces of arginine-induced currents in TgNPT1-HA-expressing oocytes, suspended in complete ND96 medium (control) and in media lacking Na+, Cl−, K+, Mg2+ or Ca2+ ions. For all current traces, the resting current before arginine addition was set to 0. Red arrows indicate the points of addition of 5 mM arginine to the ND96 medium and black arrows indicate the points at which arginine was removed. The traces are representative of n=8 oocytes under each of the conditions tested. (e) pH dependence of the maximum arginine-induced current in oocytes expressing TgNPT1-HA. Oocytes were equilibrated in media of the relevant pH and the maximum amplitude of the current following the addition of 5 mM arginine was measured. For each pH, the mean arginine-induced current is shown±s.d. (n=8; **P<0.01; n.s.=not significant; ANOVA).