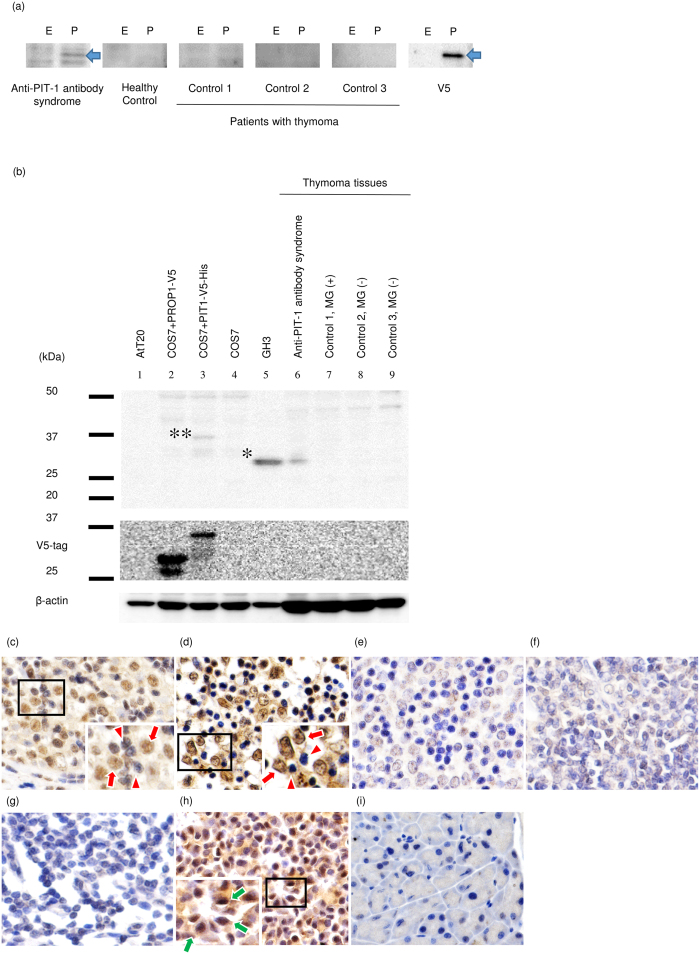
Figure 2. PIT-1 protein was aberrantly expressed in neoplastic thymic epithelial cells of the patients with anti-PIT-1 antibody syndrome.
(a) Western-blotting analysis for the detection of anti-PIT-1 antibody in the serum of patients with thymoma. E and P indicate empty vector (control) or PIT-1 expressing vector, which were transfected into COS7 cells, respectively. Arrows indicate V5-tagged PIT-1 protein. Sera were diluted 500-folds. (b) Western-blotting analysis using the lysate from thymoma tissues. PIT-1 protein was detected in the thymoma tissue of patient with anti-PIT-1 antibody syndrome (lane 6). In contrast, PIT-1 protein was not detected in the thymoma tissues from patients with MG (B2 type, lane 7) or without MG (B2 type, lane 8 and AB type, lane 9). *and **indicate endogenous PIT-1 in GH3 cells and V5-tagged PIT-1 protein in PIT-1-expressing COS7 cells, respectively. (c–g) Immunohistochemical analysis of thymoma tissues. (c) Patient 1, (d) Patient 2, (e) B2 type thymoma with MG, (f) B2 type thymoma without MG, (g) normal thymic tissue attached to thymoma with MG ( × 400), (h) mouse pituitary tissue (positive control), and (i) mouse pancreas tissue (negative control). PIT-1 protein was detected in neoplastic thymic epithelial cells (red arrow) not in lymphocytes in the 2 cases examined (red arrowhead). Green arrows indicate the PIT-1 positive cells in the mouse pituitary.