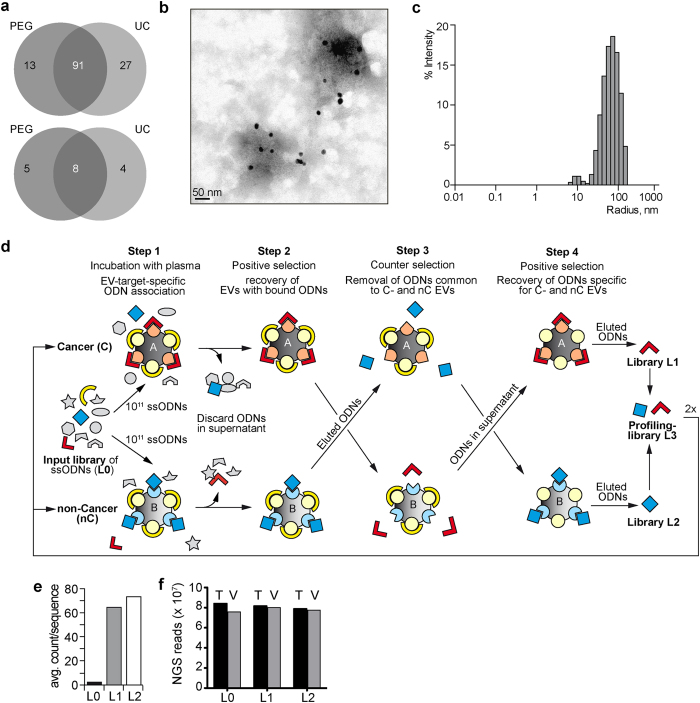
Figure 1. Generation of Profiling Library for ADAPT.
(a) Venn diagram showing the overlap between exosome-associated (top) and non-exosome-associated (bottom) proteins identified in PEG- or UC-precipitated plasma pellets. (b) TEM images of PEG precipitated exosomes (EV) visualized by anti-CD9 antibody coupled gold-nanoparticles (black spheres). (c) Dynamic light scattering (DLS) analysis of EV sizes distribution isolated by PEG precipitation. The signal decay curve as well as DLS of controls (UC purified plasma exosomes and exosome-free protein solution) are shown in Supplementary Figure 1g. (d) Library enrichment principle: a high-diversity molecule library (~1011 representatives) is contacted with blood plasma from biopsy-positive (Cancer, C) and, in parallel, with plasma from biopsy negative (non-Cancer, nC) individuals; in the 2nd step non-bound ssODNs are removed with supernatant and bound molecules are collected; in the 3rd step, ssODNs recovered from C are incubated with nC (and vice versa) and non-binders are removed with pellets; the 4th step is another binding to positive target as outlined in steps 1st and 2nd. This enrichment process was repeated three times with PCR in between: in the first iteration, UC was used to recover EVs; in the following two iterations, PEG-precipitation was used for EV recovery. A total of 119 biopsy-positive (n = 59), biopsy-negative (n = 30), and self-declared normal (n = 30) patient samples were used in the first round of L3 enrichment, while only the cancer and non-cancer samples were used in the subsequent rounds. This enrichment process delivers two separate lower-diversity libraries (~106 representatives) enriched to features (targets) present in samples A and B, respectively. (e,f) Quality and population assessment of the starting library (L0) and the respective libraries L1 and L2 obtained from (d). NGS sequence depth was similar for L0, L1 and L2 (f, grey bars: valid reads V, black bars: total reads T), whereas the number of copies per sequence was significantly increased in L1 and L2 (e), while the total number of unique sequences was reduced (Supplementary Fig.1i).