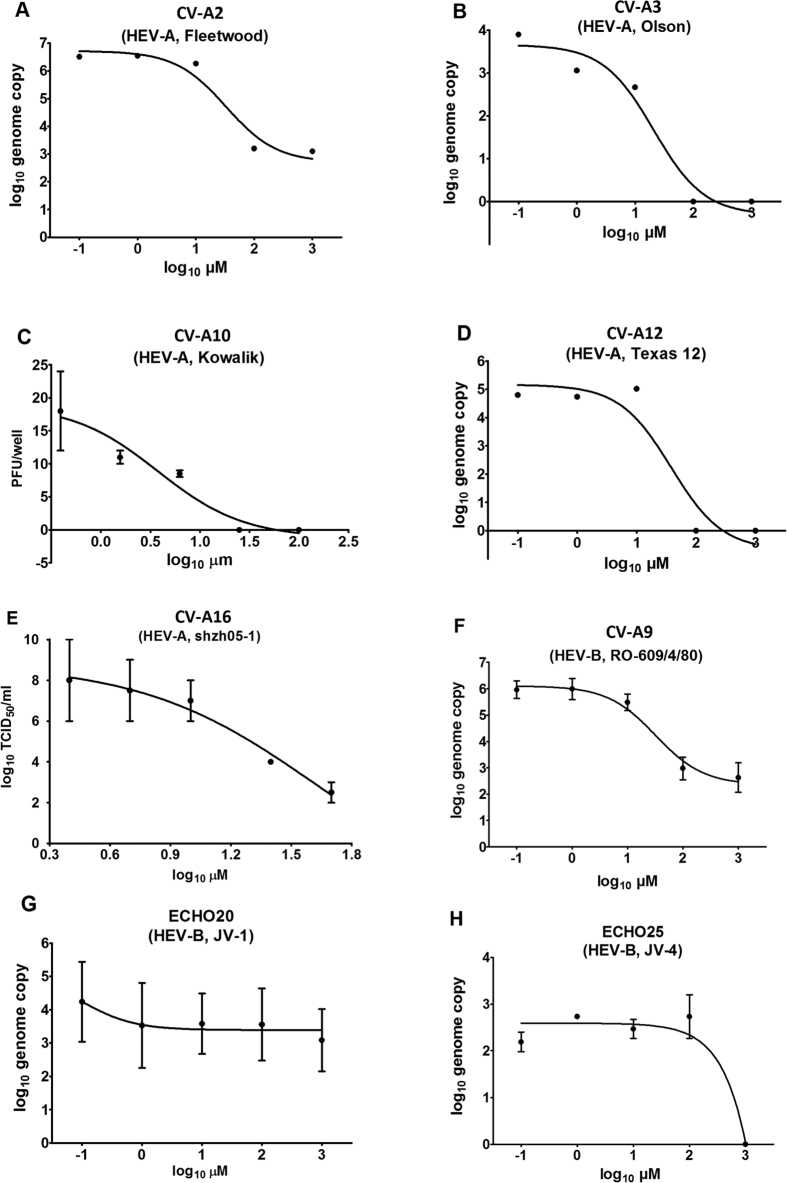
Figure 2. Suramin inhibition against HEVs.
(A) CV-A2, (B) CV-A3, (C) CV-A10, (D) CV-A12 and (E) CV-A16 are HEV-A. (F) CV-A9, (G) ECHO20 and (H) ECHO25 are HEV-B. (A,B,D,F,G,H). Inhibition was evaluated by quantitative RT-PCR. Vero cells were infected with enteroviruses at a MOI of 0.1 in 0–1000 μM suramin. The culture supernatant was collected at 46–48 hours post-infection, the RNA was extracted and the genome copy was determined by quantitative RT-PCR. (C) Inhibition against CV-A10 was tested using a plaque assay. Vero cells were infected in 12-well plates with 25 PFU/well in 0–100 μM suramin. The plaques were stained and counted after incubation for 7 days in 0.8% CMC-DMEM containing 0–100 μM suramin. (E) Inhibition against CV-A16 was evaluated in RD cells by CPE-based TCID50 titration according to a previous study12. For CV-A2, 3 and 12, each suramin concentration has only one read. Tests on CV-A10, CV-A16, CV-A9, ECHO20 and ECHO25 were performed in duplicate.