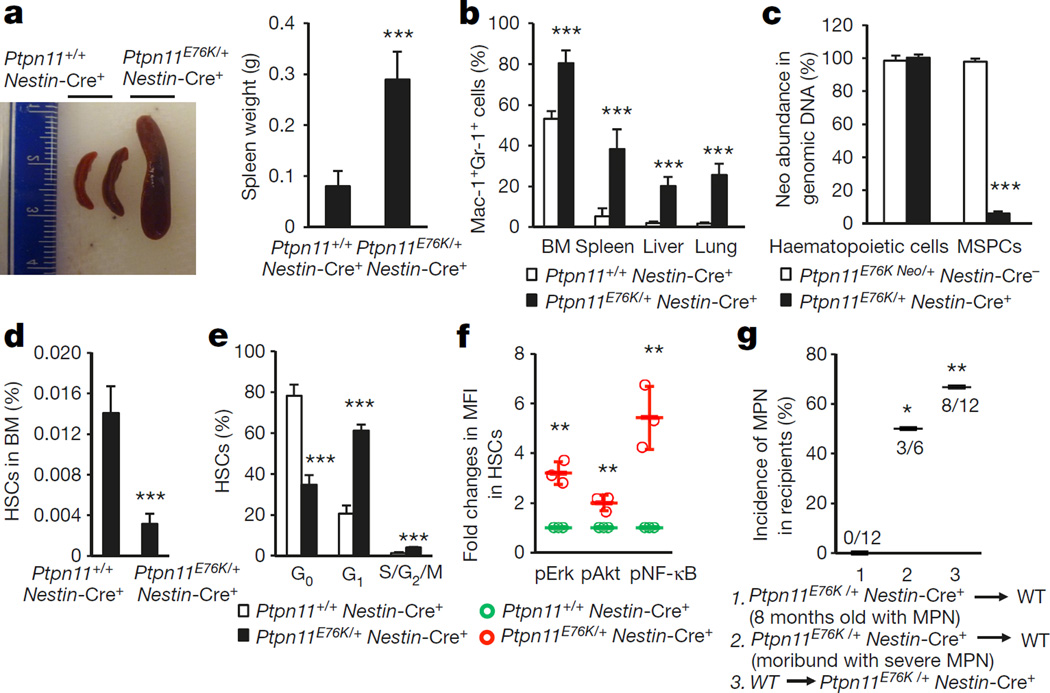
Figure 1. Ptpn11E76K/+ mutation in Nestin+ MSPCs aberrantly activates neighbouring wild-type HSCs, inducing MPN in Ptpn11E76K/+Nestin-Cre+ mice.
7–12-month-old Ptpn11E76K/+Nestin-Cre+ and Ptpn11+/+Nestin-Cre+ mice were analysed. a, Spleen weights were determined (n = 17 mice per group). b, Cells isolated from BM, spleens, livers and lungs were assayed for Mac-1+Gr-1+ myeloid cells by FACS (n = 12 mice per group). c, Genomic DNA isolated from BM haematopoietic cells and BM-derived MSPCs was assayed for the abundance of the neo cassette by qPCR (n = 5 mice per group). d–f, BM cells were assayed by multiparameter FACS to determine the pool size (n = 8 mice per group) (d), cell cycle distribution (n = 6 mice per group) (e), and intracellular signalling activities (n = 3 mice per group) (f) of HSCs (Lin−Sca-1+c-Kit+CD150+CD48−Flk2−). g, BM cells collected from 8-month old Ptpn11E76K/+Nestin-Cre+ mice (CD45.2+) with MPN or moribund Ptpn11E76K/+Nestin-Cre+ mice (12 months old) with severe MPN were transplanted into lethally irradiated wild-type mice (WT) BoyJ mice (CD45.1+). In addition, BM cells collected from BoyJ mice were transplanted into 6-month-old Ptpn11E76K/+Nestin-Cre+ mice. Recipients were monitored for MPN development for 6–8 months. Data shown in a–f are mean ± s.d. of all mice examined; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001. Source Data for this figure are available online.