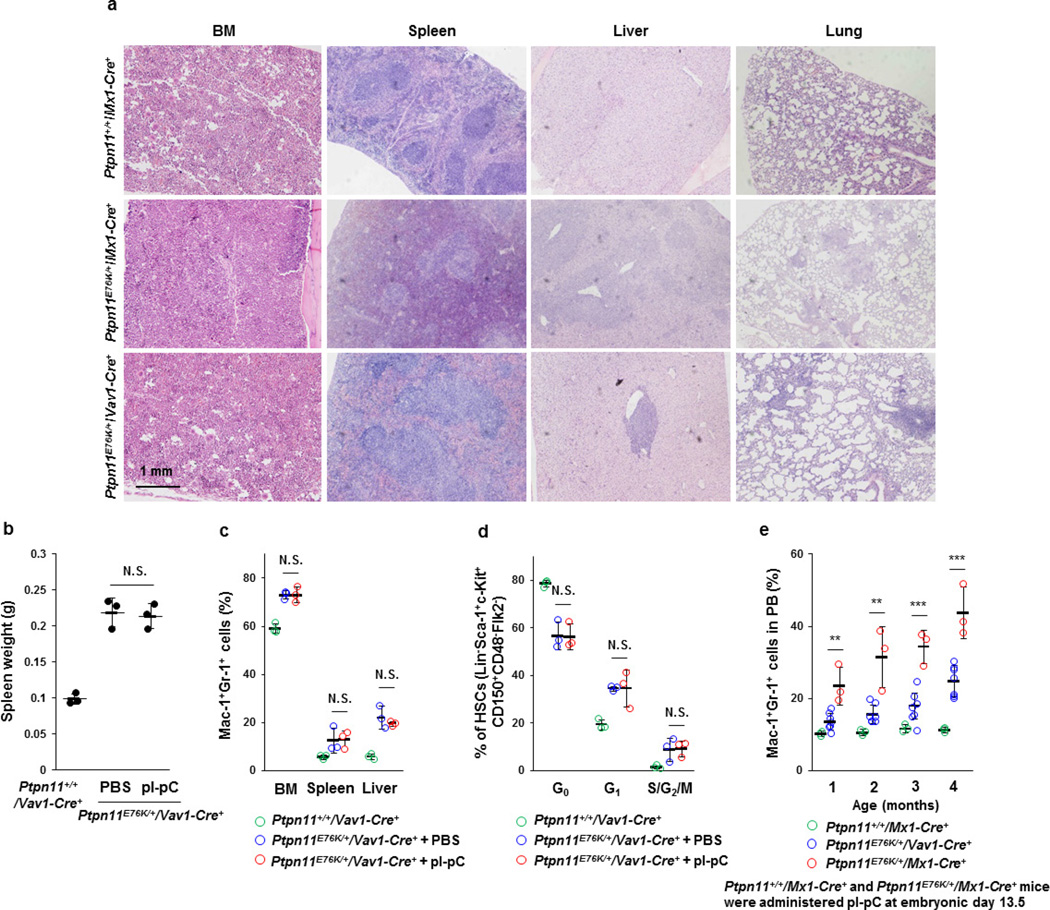
Extended Data Figure 2. Ptpn11E76K/+ mutation in the BM stroma enhances MPN development from mutant HSCs with the same mutation in Ptpn11E76K/+Mx1-Cre+ mice.
a, Tissues collected from Ptpn11+/+Mx1-Cre+, Ptpn11E76K/+Mx1-Cre+ (8 weeks after pI–pC administration), and Ptpn11E76K/+Vav1-Cre+ mice at 16-week old (n = 3 mice per group) were processed for histopathological examination (haematoxylin and eosin staining). Representative pictures are shown. b–d, Ptpn11E76K/+Vav1-Cre+ mice (4 weeks old) (n = 3 mice per group) were administered pI–pC or PBS, as described in Methods. Spleen weights (b), Mac-1+Gr-1+ myeloid cells in the BM, spleen, and liver (c), the cycling status of HSCs (d) were analysed 16 weeks after pI–pC administration. e, Timed pregnant Ptpn11E76K/+Mx1-Cre− female mice (13.5 days post coitum) that were mated with Ptpn11+/+Mx1-Cre+ male mice were administered pI–pC as above. Ptpn11E76K/+Mx1-Cre+ pups delivered by these female mice were identified. The efficiencies of neo deletion from targeted Ptpn11 alleles in haematopoietic cells and MSPCs of these mice were approximately 95%. Mac-1+Gr-1+ cells in the peripheral blood of Ptpn11+/+Mx1-Cre+ (n = 3 mice), Ptpn11E76K/+Mx1-Cre+ (n = 3 mice), and Ptpn11E76K/+Vav1-Cre+ (n = 7 mice) mice at the same age were monitored at the indicated time points. Data shown in b–e are mean ± s.d. of all mice examined; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; N.S., not significant. Source data are available online.