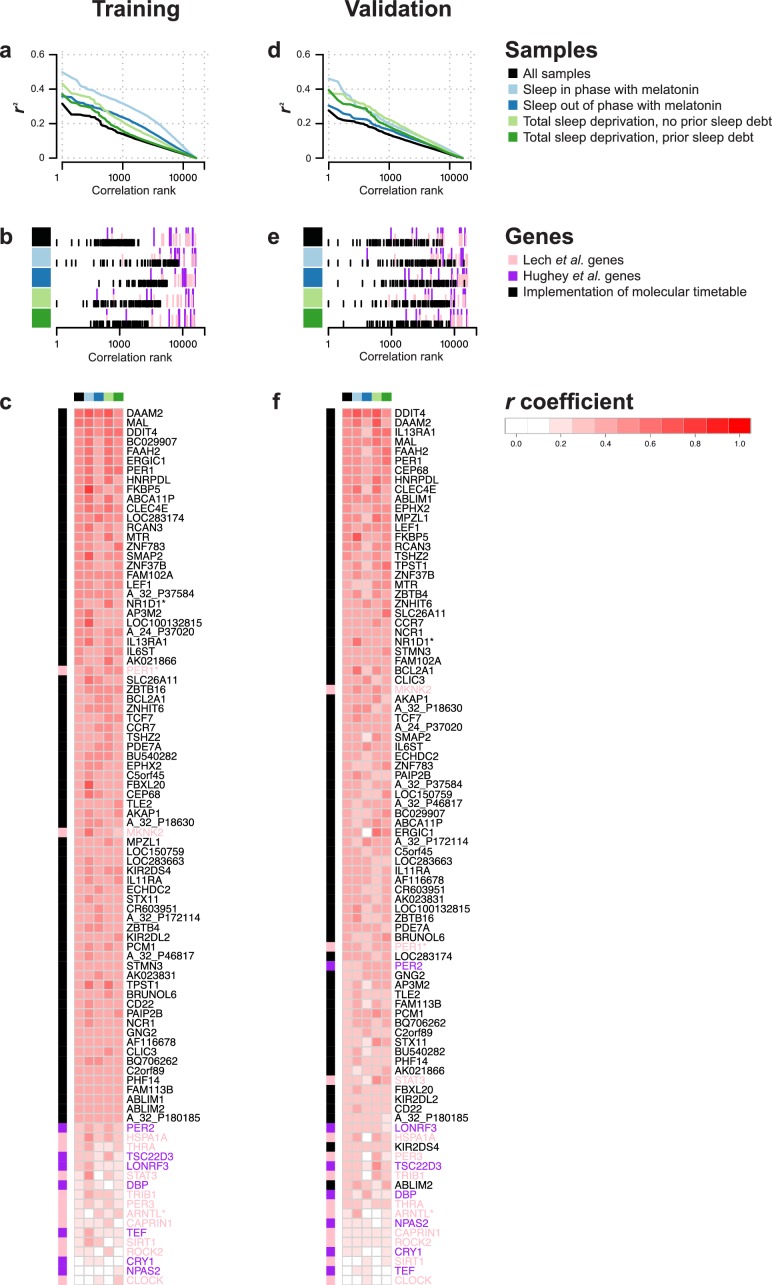
Figure 2. Rhythmicity in the conditions and identification of molecular timetable genes.
(a, d) Square of correlation value (r2) vs. rank of correlation as a measure of overall 24 hr rhythmicity in the transcriptome, separately and across conditions. For each transcript, the correlation with a cosine wave was computed, squared and the entire transcriptome was then rank-ordered separately for each conditions and across conditions. (b, e) Rank of the correlation of phase marker genes from different phase marker lists across conditions (indicated by color panel to the left) for participants in the training (b) and validation set (e). First, correlations of all ~26K features were ranked separately for conditions and training and validation set and then the rank of identified phase marker genes was identified and plotted. (c,f) Heatmap of r values of correlation between a 24 hr cosine wave and mRNA abundance profiles of a feature(s) targeting a gene identified as a phase marker by our molecular timetable, and the circadian phase marker genes published in Lech et al. (2016) and Hughey et al. (2016). Correlations were computed separately for each of the four conditions (indicated by the color panel at the top of the heatmap) and all conditions combined for the training (c) or validation set (f). Rows in the heatmap are ordered based on the correlation column for the ‘all conditions’ dataset, that is, the column indicated with black. Data source files: Figure 2—source data 1.
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.20214.003