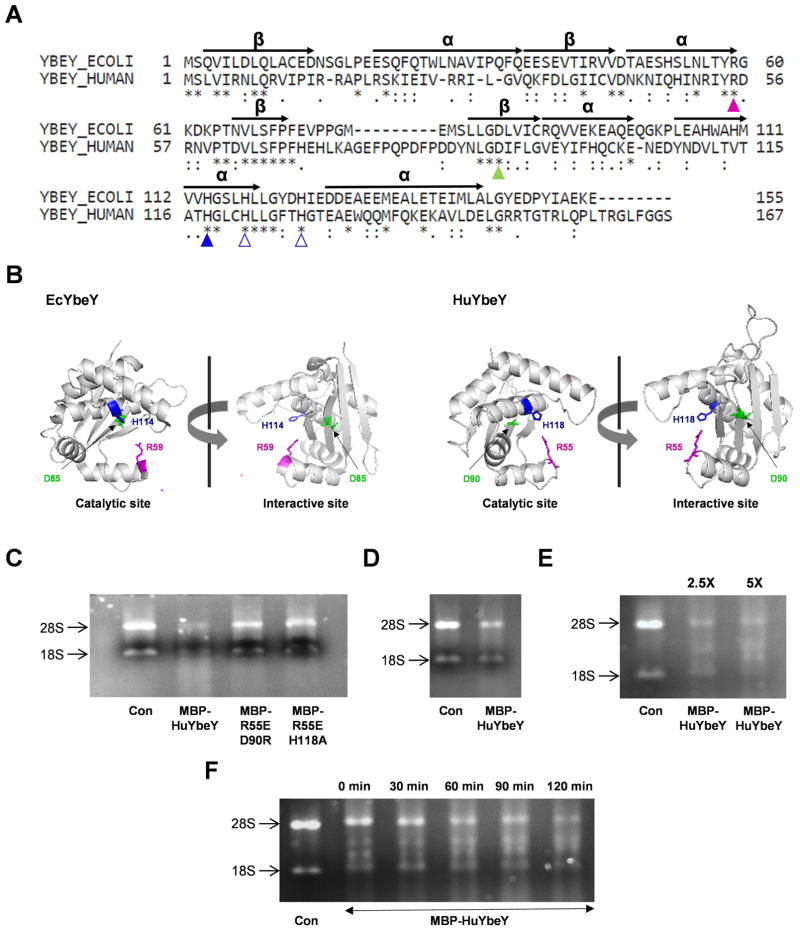
Fig 1. Characterization of human YbeY, C21orf57 (HuYbeY).
(A) Protein sequence alignment of EcYbeY and HuYbeY. α-helices (α) and β-sheets (β) are indicated based on the crystal structure analysis of EcYbeY [10]. (B) PyMOL presentation of EcYbeY (PDB: 1XM5;[10]) showing the catalytic domain (left) and ribosome-binding domain (right). HuYbeY was modelled onto the coordinates of EcYbeY using SWISS-MODEL [6]. EcYbeY residues R59 (magenta), D85 (green) and H114 (blue) correspond to HuYbeY residues R55, D90 and H118, respectively, in (A) and (B). (C)-(F) MBP-HuYbeY degrades total human RNA. (C) RNase activity of MBP-HuYbeY protein in comparison to the mutated forms of MBP-HuYbeY protein; 1 μM concentration of protein was used. RNA was digested with 1 μM (D), 2.5 and 5 μM (E) concentration of MBP-HuYbeY protein, while the time-course assay was performed with 5 μM concentration of MBP-HuYbeY protein (F). Wild-type and mutant MBP-HuYbeY proteins in (C) have been purified from E. coli BL21(DE3) plysS Δrna strain; MBP-HuYbeY in (D, E and F) has been purified from E. coli BL21(DE3) plysS Δrna Δpnp strain. RNA digests were analyzed by agarose gel electrophoresis.