Fig. 1.
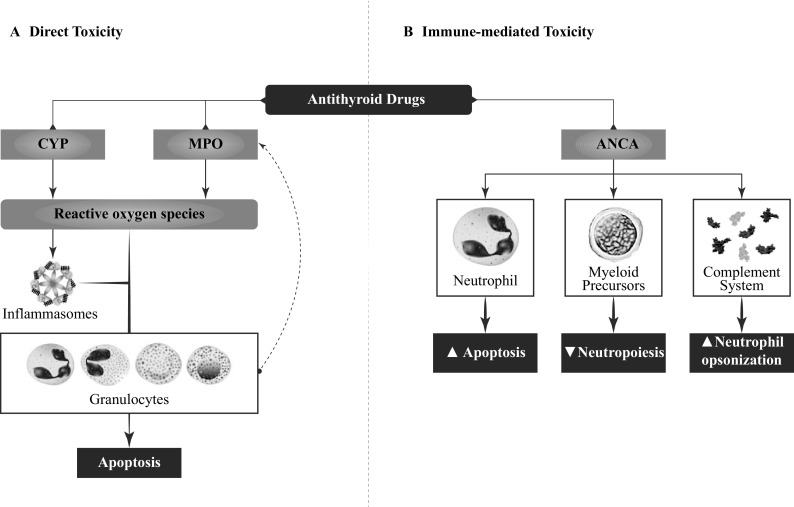
Mechanisms behind the onset of antithyroid drug-induced agranulocytosis. a Direct toxicity: the oxidative process of the antithyroid drug is mediated by myeloperoxidase and cytochrome P450, generating reactive metabolites that will induce apoptosis either directly or via inflammasomes. b Immune-mediated toxicity: anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies may react against neutrophil antigens as proteinase 3, myeloperoxidase, and cathepsin G after neutrophils are primed and antigens migrate to the cell membrane. Anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies can also induce opsonization of neutrophils mediated by the complement system and react with myeloid precursors. ANCA anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies, CYP cytochrome P450, MPO myeloperoxidase
