Figure 1.
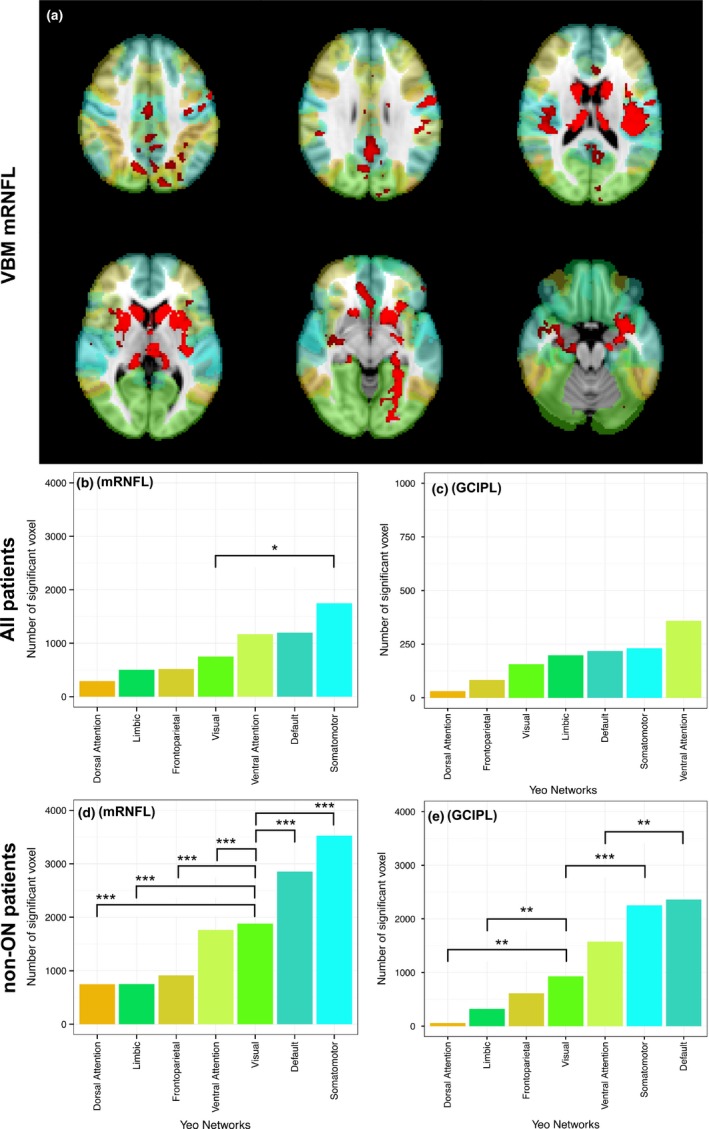
VBM: Significant voxels in functional networks. Association between macular RNFL and GCIPL thickness within a 3 mm cylinder centered at the fovea centralis and functional networks (Yeo cortical atlas). (a) Example of VBM results for mRNFL, colors represent network regions according to the barplots below, significant VBM results are in red, displayed on MNI152 standard. Barplots show median values from left and right eyes. Absolute number of significant voxels associated with macular RNFL (left, b and d) and GCIPL (right, c and e). Results derive from all patients (upper, b and c) and patients without a history of optic neuritis (non‐ON, lower, d and e). Significance of differences (*=p < .05, **=p < .01, ***=p < .001) estimated with GEE models (visual network as reference category)
