Figure 1.
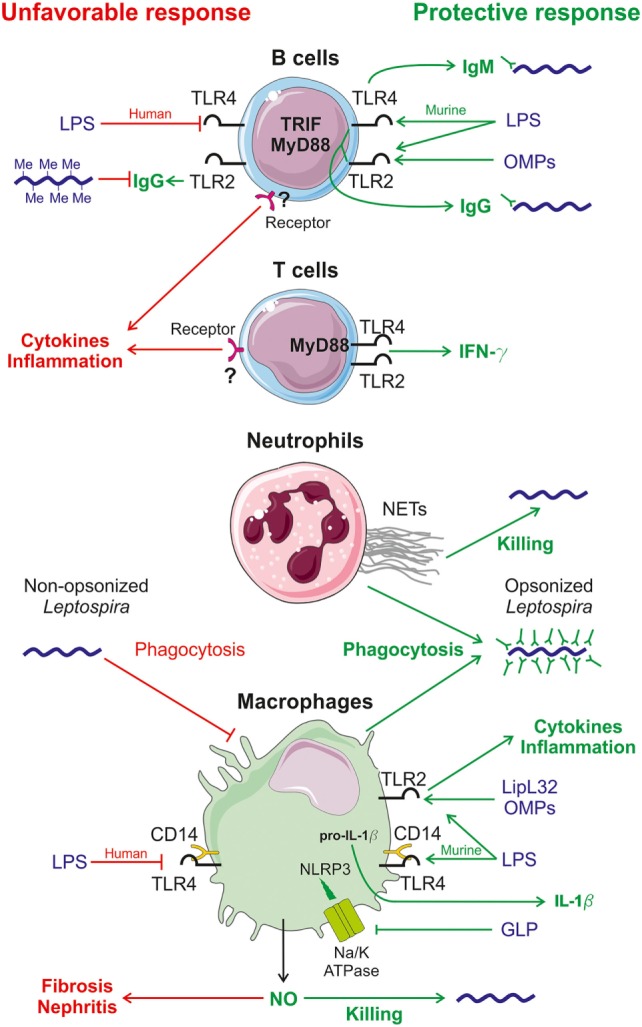
Diagram of immune responses induced by Leptospira sp. infection in mice. Known innate responses to Leptospira sp. involve neutrophils, macrophages but also B and T cells. Recognition of Leptospira sp. mostly occurs through the TLR2 pathway, sensing outer membrane proteins (OMPs) such as the lipoprotein LipL32, the major leptospiral OMP and the atypical LPS (72), which is also recognized by toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) in mice (73). Protective host responses are depicted in green on the right side, whereas potential unfavorable responses are in red, on the left side. In mouse B cells, TLR4 stimulation by leptospiral LPS leads to the early production of partially protective IgM (44), via the TRIF adaptor (74). TLR2 and TLR4 responses, through the Myd88 adaptor, also control the production of protective IgG (44). In vivo methylation of LipL32 in rat has been shown to reduce its recognition by human antiserum (78). In humans, leptospiral LPS is not recognized by TLR4 (73), potentially leading to disease, as observed with TLR4 mutant mice (39, 44, 63). In mouse T cells, Leptospira interrogans signal through the MyD88-dependent activation of TLR4 and TLR2 receptors and trigger the production of the protective pro-inflammatory cytokine IFN-γ that activates macrophages (44). Both T and B cells, by sensing leptospiral components through an unknown receptor, are involved in the production of an unfavorable pro-inflammatory cytokine response (44). In humans, neutrophils play a slight protective role for the host against Leptospira sp. infection due to the production of bactericidal neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) (66). Neutrophils and macrophages barely phagocytize non-opsonized Leptospira sp. but opsonized Leptospira sp. with specific IgG are readily killed by phagocytose (43, 82). Macrophages produce pro-inflammatory cytokines leading to a protective inflammatory state by sensing OMPs, including LipL32, via TLR2 (72). The atypical leptospiral LPS is also detected by TLR2 and CD14, the co-receptor of TLR4 (72). Acting in concert with TLR2 and TLR4 activation, leptospiral glycoprotein blocks the Na/K-ATPase pump that triggers the activation of the Nod-like receptor protein 3 (NLRP3) inflammasome and enables the secretion of the pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-1β (65). Upon L. interrogans infection, macrophages and other cells also produce nitric oxide (NO), which has a positive and a negative effect. NO has a protective effect through the action of its antimicrobial role (67) and the negative effect is that NO activity favors kidney fibrosis (36) and nephritis of infected hosts (35, 67).
