Figure 6.
Induction of a Myeloid Lineage Phenotype in Transformed B Cell Precursors Causes DNA Damage at Myeloid-Specific Genes
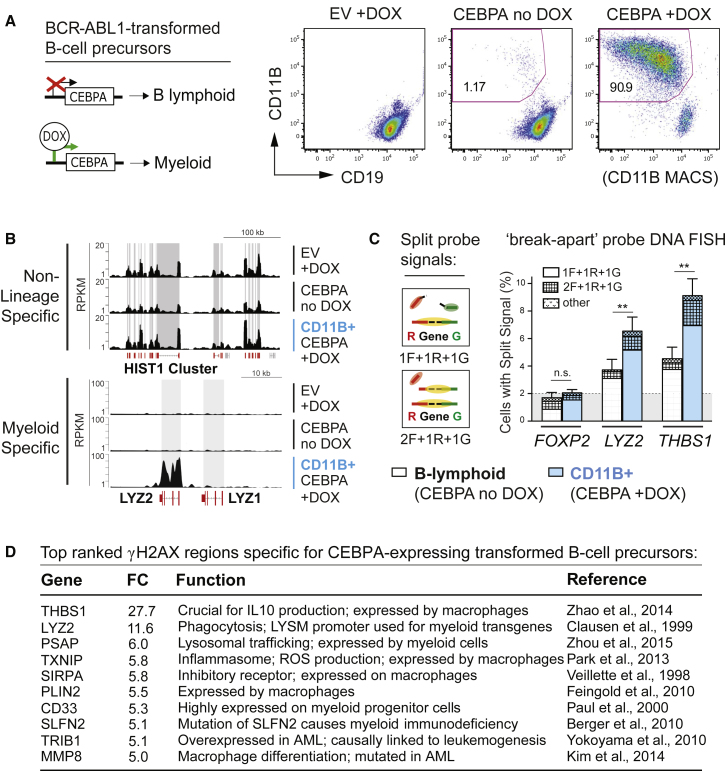
(A) Left: Schematic of the experimental strategy for induction of a myeloid phenotype in transformed B cell precursors using DOX-inducible CEBPA expression. Right: DOX/CEBPA-mediated induction of the myeloid phenotype verified by flow cytometry using CD11B as a myeloid lineage and CD19 as a B lymphoid lineage marker. EV-transduced lymphoid leukemia cells were used as a control. Anti-CD11B magnetic bead based cell sorting (MACS) was performed on DOX-treated cells with inducible CEBPA to reach a purity of >90% CD11B-positive cells for ChIP-seq analysis.
(B) Custom track visualization of γH2AX read densities for non-lineage-specific (HIST1 cluster, top) and myeloid lineage-specific gene loci (LYZ2, bottom). Grey boxes indicate gene-body location of the indicated gene.
(C) Assessment of myeloid γH2AX ChIP-seq hotspots identified in CEBPA + DOX cells using DNA FISH and break-apart probes as described in Figure 2C. Results of five independent experiments for LYZ2 and THBS1 (myeloid γH2AX hotspots) versus FOXP2 (coldspot) are shown (data represent mean ± SEM).
(D) Table of the ten top-ranked genes with significant γH2AX signals specific for CEBPA + DOX cells (by fold change). Full references can be found in the Supplemental Information.