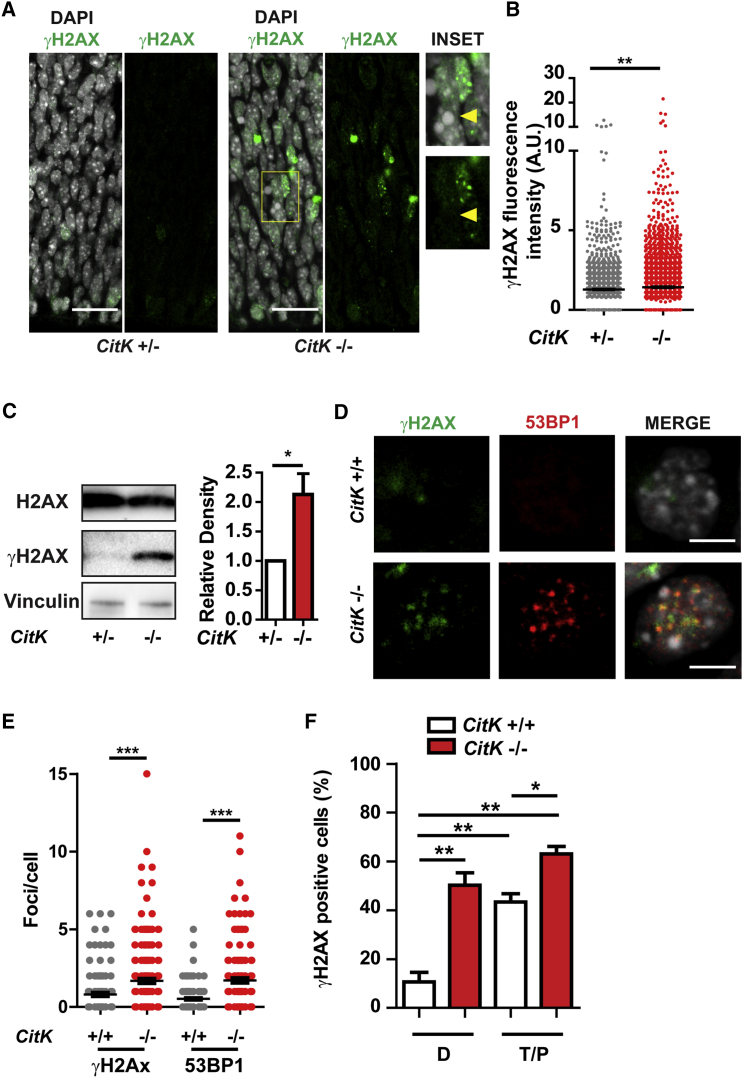
Figure 1.
CITK Prevents DNA Damage Accumulation in the Developing Nervous System
(A) Cerebral cortex sections of E14.5 mouse embryos stained anti-γH2AX antibodies and DAPI. The scale bars represent 25 μm.
(B) Quantification of γH2AX fluorescence intensity per cell in sections obtained as in (A).
(C) Western blots of cell lysates from P4 cerebella of CitK −/− and control mice (+/+ and +/−) probed with anti-H2AX and anti-γH2AX antibodies. Quantification of the γH2AX/H2AX ratio is shown.
(D) NPCs from E12.5 embryo cortices stained for γH2AX (green), 53BP1 (red), and DNA (DAPI, blue). The scale bars represent 10 μm.
(E) Quantification of γH2AX foci or 53BP1 foci per cell in NPCs.
(F) Cells stained as in (D) were classified as diploid (D) or tetraploid/polyploid (T/P) by quantification of the DAPI signal (see Experimental Procedures) and as γH2AX positive if they displayed more than five foci/cell.
Two tails unpaired Student’s t test was used for the statistical analysis of these experiments (n = 3–6 per group). Graphs show mean ± SEM. ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.001.