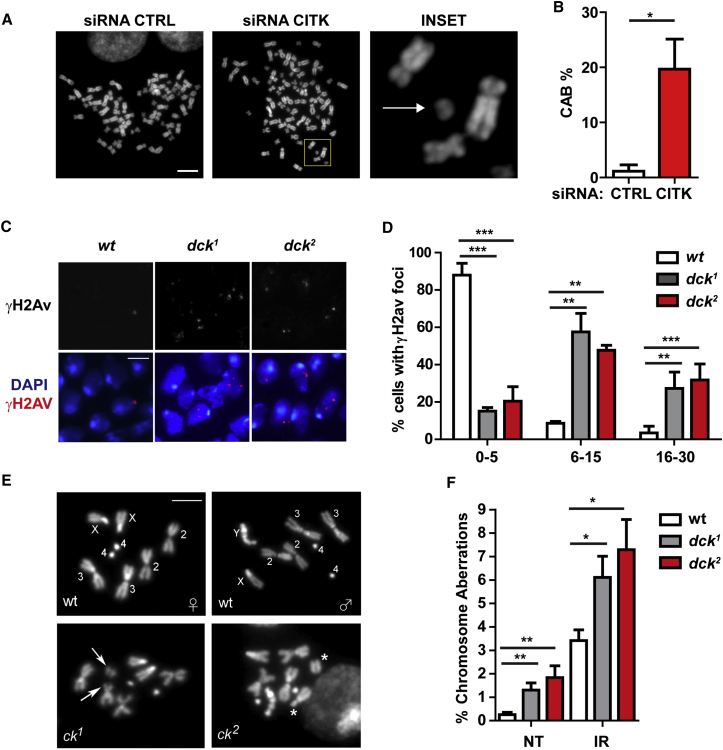
Figure 2.
CITK Has a Phylogenetically Conserved Role in Maintenance of Genome Integrity
(A) DAPI-stained metaphase spreads from control and CITK-depleted ONS-76 cells. An acentric isochromatid fragment is indicated in the inset (arrow).
(B) Frequencies of CABs in mock-treated or CITK-depleted ONS-76 metaphases.
(C) Drosophila brain squashes from wild-type (wt) dck1 and dck2 mutant larvae stained with anti-γH2Av antibodies and DAPI.
(D) Frequencies of negative (0–5 γH2Av foci/cell), moderately positive (6–15 foci/cell), or strongly positive (>15 foci/cell) cells in the samples shown in (C).
(E) Diploid DAPI-stained metaphase spreads from control (wt) and mutant (dck1 and dck2) Drosophila larval brains showing broken chromosomes (arrows and stars).
(F) Frequencies of chromosome aberrations (CABs) in untreated (NT) or irradiated (IR) (4Gy of X-rays) diploid larval brain cells from wild-type or dck mutant larvae.
The scale bars in (A) and (C) represent 5 μm. Two tails unpaired Student’s t test was used for the statistical analysis of these experiments (n = 3–4 per group). Graphs show mean ± SEM. ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.001.