Figure 6.
Homing of HSPCs to BM Sinusoidal Capillaries
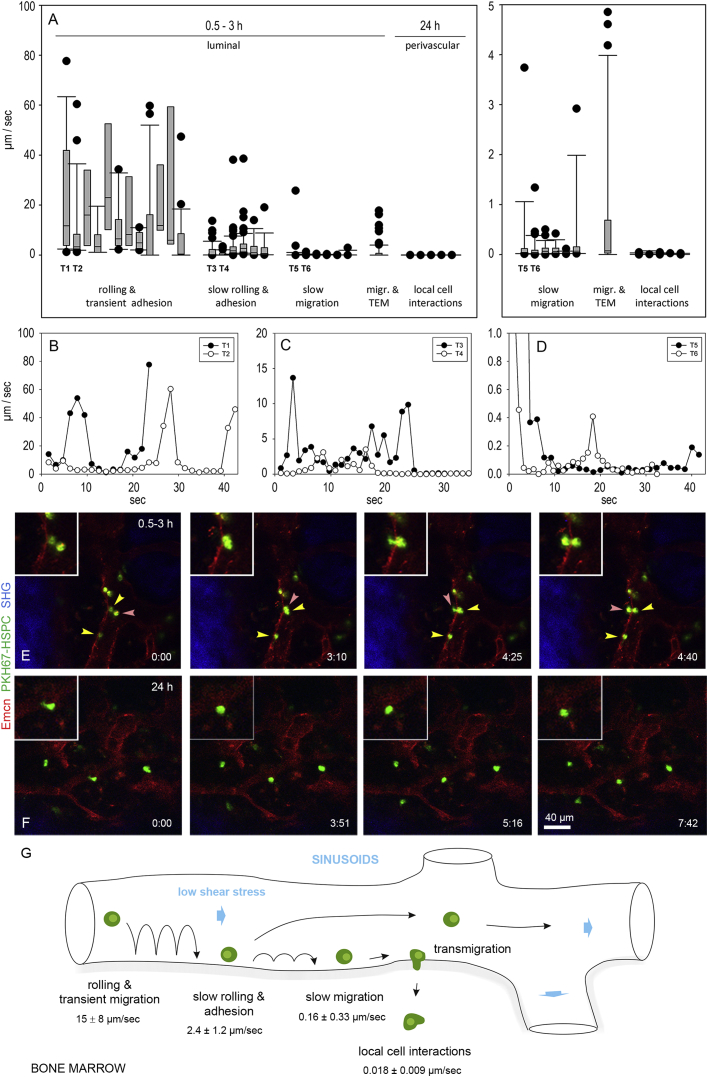
(A) Micrograph showing velocities of individual HSPC tracks during rolling and transient adhesion, slow rolling and adhesion, slow migration, and transmigration 0.5–3 hr after intravenous injection of fluorescently labeled HSPCs. After 24 hr, HSPC reside in the BM cavity in proximity to sinusoidal capillaries. Zoom-in view is on the right.
(B–D) Velocity-time graphs of two representative tracks for rolling and transient adhesion (B, T1 and T2 in A showing slow rolling and adhesion; C, T3 and T4 in A showing slow rolling and adhesion; D, T5 and T6 in A showing slow migration). Bars represent mean values ± SD, 15 vessels segments were analyzed from n = 7 animals.
(E and F) HSPC transmigration and local cellular interaction in the BM compartment. (E) Fluorescently labeled BM lineage-depleted HSPC (green) transmigrated across the Enmc+ endothelium of BM sinusoids (red) after rolling and a short adhesion phase as visualized by in vivo two-photon imaging; time in minutes (Movie S9). Red arrowheads follow luminal adhering HSPC to a perivascular position close to the sinusoidal endothelium. Yellow arrowheads point toward adhering or slowly migrating HSPCs. Note that transmigration event is initiated by a single protrusion that projects through the endothelium. Within ∼1.5 min, the HSPC translocates its cell body through the endothelium to a perivascular position in the BM cavity. Note that two transmigration events from two animals are reported (Figure S3C). (F) Several HSPCs (green) reside in the BM compartment in close proximity to Enmc+ sinusoidal capillaries (red). Most HSPCs reside stationary or migrate very slowly and show local cell membrane protrusions behavior (arrows) indicating active cell interactions; time is in minutes (Movie S10).
(G) Schematic illustrating the multistep process of HSPC homing with mean velocities for individual steps. Bars represent mean values ± SD, 15 vessels segments were analyzed from n = 7 animals.