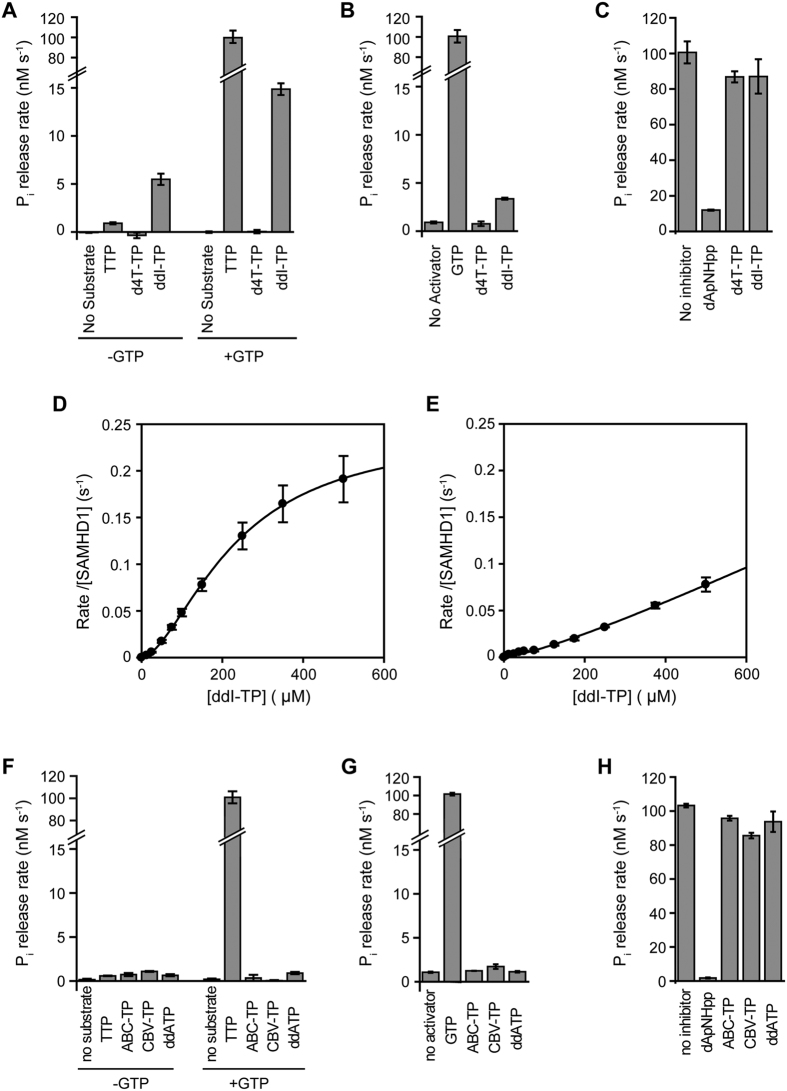
Figure 1. The effects of d4T-TP,ddI-TP,ddA-TP, ABC-TP and CBV-TP on SAMHD1 triphosphohydrolase activity.
(A) Hydrolysis of 0.3 mM TTP, d4T-TP or ddI-TP in the absence (left) and presence (right) of 0.1 mM activator GTP. (B) Activation of SAMHD1 TTP hydrolysis. Triphosphohydrolase activity was measured with 0.3 mM TTP substrate upon addition of 0.1 mM GTP, d4T-TP or ddI-TP as activators. (C) Inhibition of SAMHD1 GTP-activated TTP hydrolysis. Triphosphohydrolase activity was measured with 0.3 mM TTP and 0.1 mM GTP activator alone and with addition of 0.3 mM dApNHpp positive control, d4T-TP or ddI-TP. Error bars are the standard error of the mean (SEM) of three independent measurements. (D) Concentration dependence of SAMHD1 ddI-TP hydrolysis in the presence of 0.2 mM GTP (saturating activator concentration). Nonlinear least squares fitting using a Hill equation gives the apparent binding constant KS = 226 ± 12 μM, catalytic constant kcat = 0.24 ± 0.04 s−1 and the Hill coefficient n = 1.7 ± 0.1 (Mean ± SEM). (E) ddI-TP allosteric activation of TTP hydrolysis. Rates were determined for 1 mM TTP at varying dd-ITP concentration. Nonlinear least squares fitting gives only lower estimates for the maximal rate and the ddI-TP concentration at half maximal activation of kmax > 0.1 s−1 and Ka > 300 μM. (F) Hydrolysis of 0.3 mM TTP, ABC-TP, CBV-TP and ddATP in the absence (left) and presence (right) of 0.1 mM activator GTP. (G) Activation of SAMHD1 TTP hydrolysis. Triphosphohydrolase activity was measured with 0.3 mM TTP substrate upon addition of 0.1 mM GTP, ABC-TP, CBV-TP or ddATP as activators. (H) Inhibition of SAMHD1 GTP-activated TTP hydrolysis. Triphosphohydrolase activity was measured with 0.3 mM TTP and 0.1 mM GTP activator alone and with addition of 0.3 mM dApNHpp positive control, ABC-TP, CBV-TP or ddATP. Error bars are the range of data from two independent measurements.