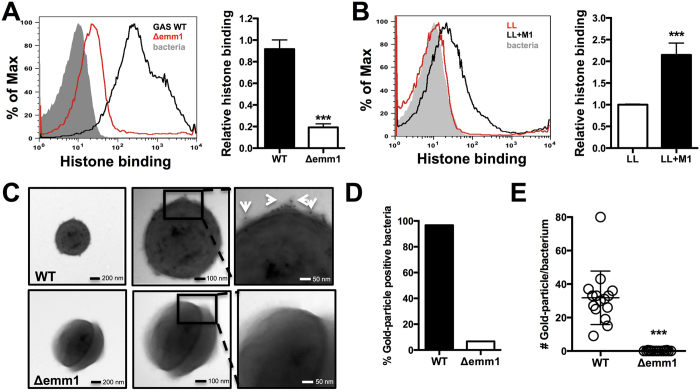
Figure 5. M1 protein binds to and sequesters histones.
(A) Binding of histone H2A at 31.25 μg/mL to whole, live GAS M1 WT and Δemm1 mutant bacteria was determined via IHC using primary anti-histone H2A antibody followed by secondary Alexa 488 antibody by shift in fluorescence intensity by flow cytometry and quantified using the geometric mean fluorescence intensity (gMFI). (B) Binding of histone H2A was analyzed for whole, live LL WT and LL+pM1 bacteria by flow cytometry and quantified by gMFI. Visualization of histone binding to the most surface-exposed protein from GAS, the M1 protein (hair-like structures) of GAS M1 WT and Δemm1 mutant (C) using primary rabbit anti-histone H2A antibodies followed by secondary anti-rabbit immunogold-labeled antibodies visualizing 15 nm gold particle with white arrows by transmission electron microscopy (TEM). (D) Qualitative binding of histones as determined by identification of immune-gold positive bacteria and quantification of immune-gold particle number per bacterium were determined from > 20 bacteria in random view fields at a 49,000x magnification. Results in (A–C) show representative results or TEM images from at least three independent experiments. Quantification of results obtained by flow cytometry in (A,B,E) represent average ± SEM values and were analyzed by Student’s t-test (***P < 0.001).