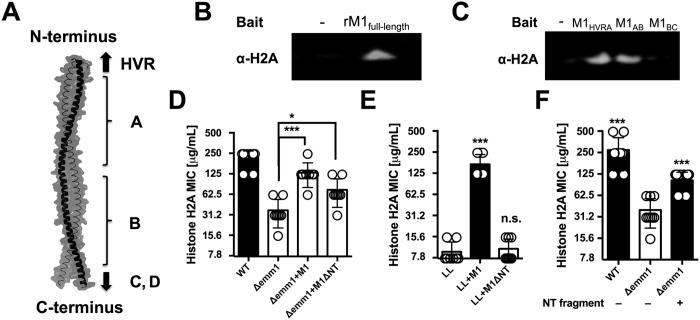
Figure 6. N-terminal portion of M1 protein binds to histones and mediates resistance against histones.
(A) Schematic of M1 protein (2OTO) model highlighting the N-terminal hyper-variable region (HVR), and A and B repeat and the start of the C and D repeat which terminate at the C-terminal cell wall anchor. (B) Full length, recombinant M1 protein (rM1full-length) was used as bait to analyze interaction with histone H2A as determined by pull-down analysis and developed by western blot. (C) Binding of recombinant, truncated rM1 fragments HVR+A, A+B or B+C part of M1 protein to histone H2A by pull-down was visualized by western blot. (D) GAS M1 WT, Δemm1 mutant, Δemm1+pM1 and a complemented strain lacking the NT region (Δemm1+pM1ΔNT) were tested for resistance to histone H2A by MIC as well as (E) LL WT, LL+pM1 and LL+pM1ΔNT. (F) Effect of exogenous 10 μM NT fragment on histone killing for GAS Δemm1 mutant in MIC testing. Results shown were obtained from at least three independent experiments. Results shown represent average ± SEM values and were analyzed by Mann-Whitney test in (D–F) (*P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001).