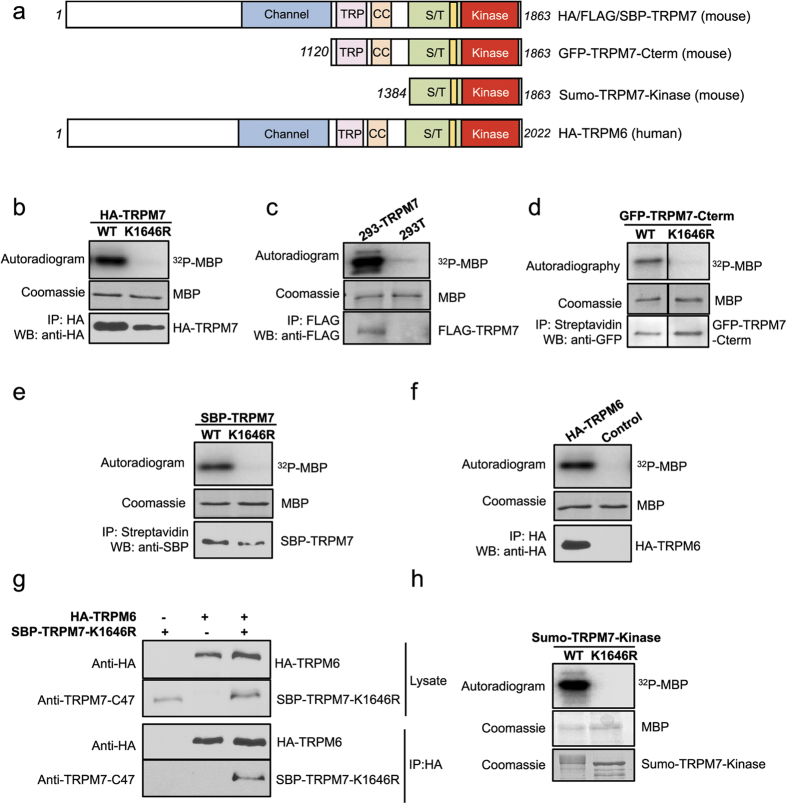
Figure 1. TRPM7 and TRPM6 constructs employed for phosphorylation analysis.
(a) Schematic diagrams showing the domain organization of TRPM7 and TRPM6. Between the ion channel (blue) and the functional alpha-kinase domain (red) there reside a conserved TRP box (purple), a coiled-coil domain (orange), a serine/threonine-rich domain (green), and an exchange-segment of the kinase (yellow). Two additional TRPM7 constructs were generated: a GFP-tagged mouse TRPM7 C-terminus protein (a.a. 1120–1863) (GFP-TRPM7-Cterm) and a Sumo-tagged mouse TRPM7 fragment containing the S/T-rich and kinase domains (a.a. 1384–1683) (Sumo-TRPM7-Kinase). TRP = TRP box, CC = coiled-coil domain, S/T = serine/threonine-rich domain. (b–f) Various TRPM7 and TRPM6 proteins were purified from mammalian cells as described in the Material and Methods. The kinase activities of purified proteins were assessed in vitro with kinase assays using myelin basic protein (MBP) as a substrate, and the assays were performed at 30 °C for 20 min. The proteins were resolved by SDS-PAGE and Coomassie blue staining. 32P incorporation into MBP was detected by autoradiography. The presence of each kinase in the sample was verified by western blotting. (g) Co-immunoprecipitation assay confirms the heteromeric TRPM6/7 complex formation. A kinase-inactive SBP-TRPM7-K1646R was co-expressed with HA-TRPM6 in HEK-293T cells and pulled down by HA-agarose. Proteins in the lysate and the immunoprecipitated samples were resolved by SDS-PAGE and analyzed by western blotting. (h) Sumo-TRPM7-Kinase WT and K1646R were purified from E. Coli as described in the Materials and Methods. Their catalytic activities were tested in vitro in a kinase assay using MBP as a substrate and the assays were performed at 30 °C for 2 min.