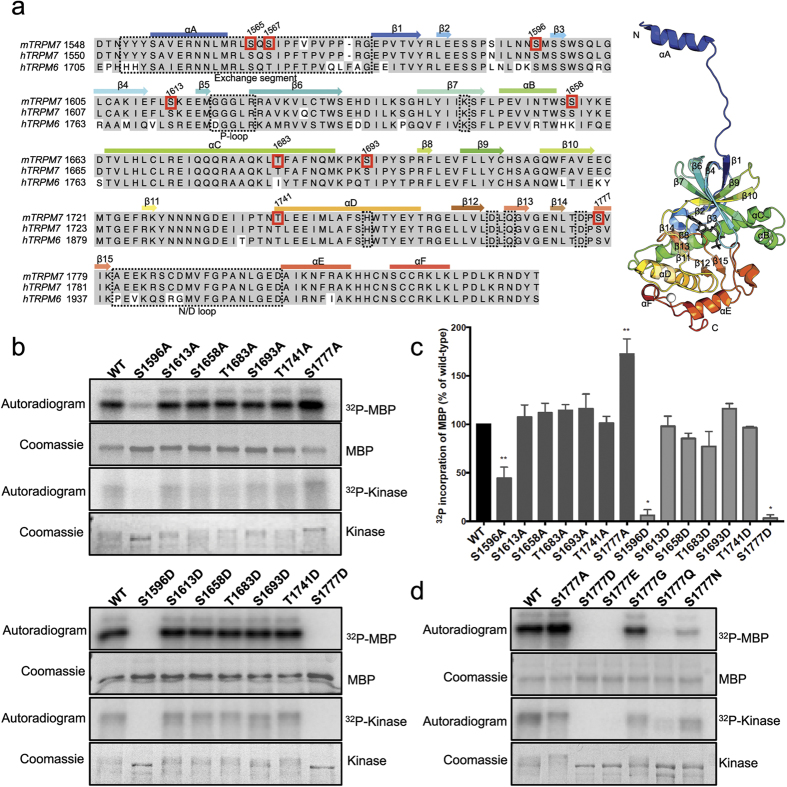
Figure 5. Mutagenesis screen of TRPM7 kinase domain phosphorylation sites.
(a) Sequence alignment of mouse TRPM7, human TRPM7, and human TRPM6 (UniProtKB: Q923J1, Q96QT4, and Q9BX84). The position of α-helices (boxes) and β-strands (arrows) are shown above the alignment. Functionally important motifs and resides on the mouse TRPM7 sequence are shown in dashed boxes. Seven identified autophosphorylation residues on the mouse TRPM7 sequence are shown in red boxes. On the right, a ribbon diagram depicts the structure of mouse TRPM7 kinase domain (PDB code 1IA9). The AMPPNP is rendered as gray sticks and the zinc atom as a white sphere. The N- and C-termini are indicated as “N” and “C”. (b) Sumo-TRPM7-Kinase WT and mutants were purified from E. Coli as described in the Materials and Methods. Catalytic actives of the WT and mutant kinases were assessed in in vitro kinase assays using MBP as a substrate. The kinase assays were performed at 30 °C for 2 min. (c) Quantification of 32P incorporation into MBP is shown as a histogram. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. Results are means ± S.E.M (n = 2–9). (d) The catalytic activities of Sumo-TRPM7-Kinase WT and various S1777 mutants were assessed by an in vitro kinase assay as described in the Materials and Methods. The kinase assays were performed at 30 °C for 2 min.