Figure 1.
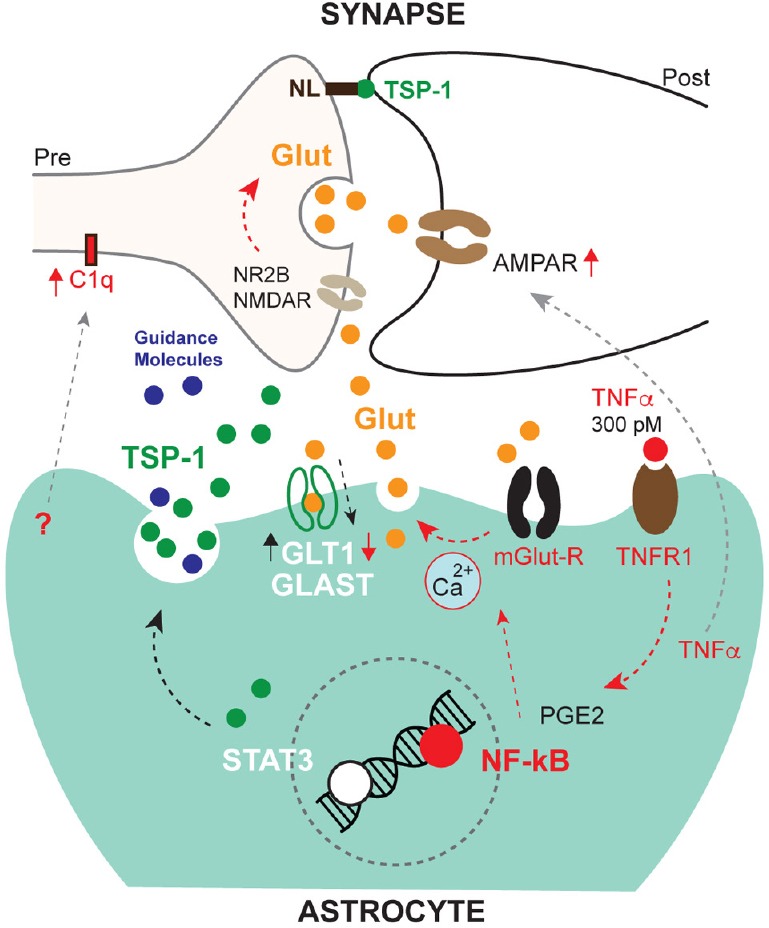
Effects of astrocyte mediated inflammatory responses on synapses.
TNFα signals via TNFR1/NF-κB and facilitates glutamatergic synaptic excitation by several mechanisms. This is detrimentally overactivated (red arrows) by TNFα at higher concentrations than 300 pM, which also impedes compensatory glutamate uptake by downregulating glial glutamate transporter-1 (GLT1). This inflammatory response is also conducive to a response characterised by synapse removal, involving the complement system (C1q). On the contrary, STAT3 signalling induces a synapse recovery process and may help excess glutamate uptake by GLAST (black arrows). Less characterized mechanisms are indicated by gray arrows. GLAST: Glutamate aspartate transporter; Glut: glutamate; mGlut-R: metabotropic glutamate receptor; NL: neuroligin; NR2B: NMDAR subunit; PGE2: prostaglandin E2; TNFR1: tumor necrosis factor-receptor1; TNFα: tumor necrosis factor-α.
