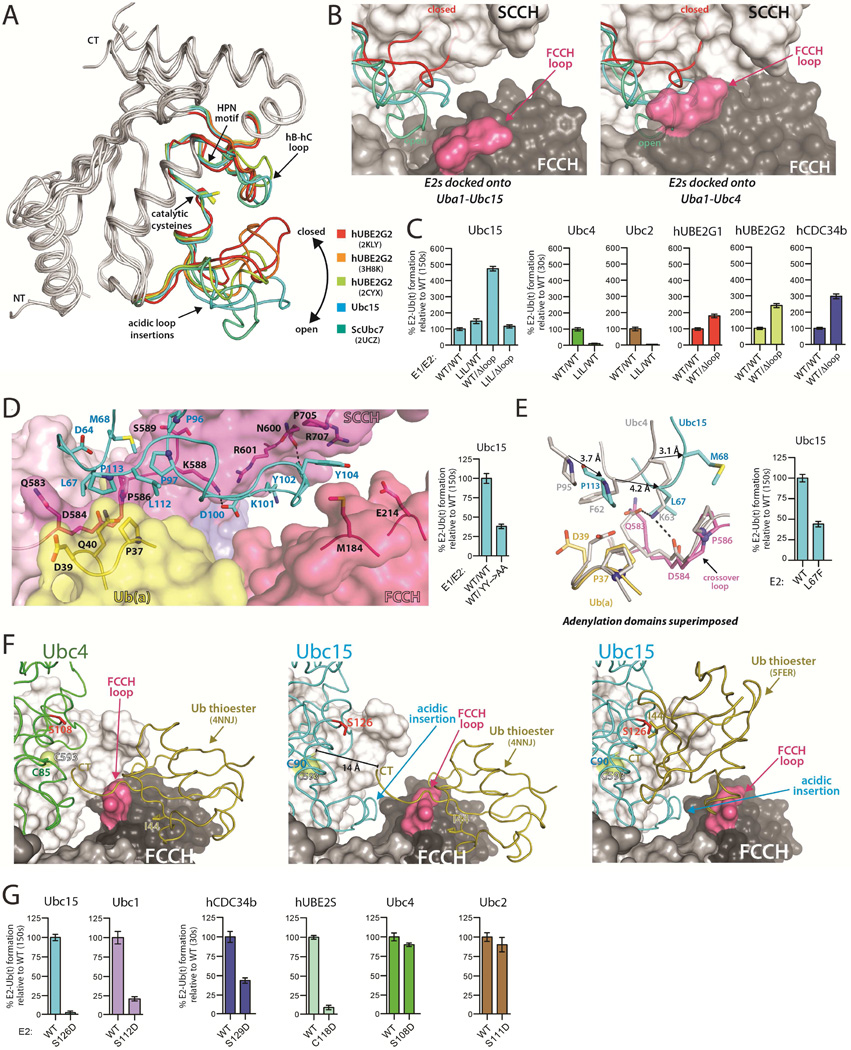
Figure 2. The Ubc15 acidic loop and architecture of the 'doubly loaded' Ub E1-E2 complex.
(A) The UBC domains of the indicated E2s were superimposed with the acidic loop insertions color-coded as indicated.
(B) The indicated E2s were superimposed onto the Uba1-Ubc15 structure (left) and Uba1-Ubc4 structure (right). E2s colored as in A.
(C) E1-E2 thioester transfer assays of the indicated proteins. Δloop indicates family three E2 constructs with the acidic loop deleted. LIL indicates a Uba1 mutant harboring an eleven amino acid insertion in the FCCH loop. Error bars in all figures represent ±1 standard deviation and were derived from three independent experiments.
(D) Uba1-Ubc15 structure colored as in Figure 1C with residues involved in key intermolecular contacts shown as sticks (left). E1-E2 thioester transfer assays of the indicated proteins (right).
(E) Uba1-Ubc15 and Uba1-Ubc4 structures shown as in Figure 1G with equivalent E2 residues that occupy different locations at the E1-E2 interface indicated by a black arrow. E1-E2 thioester transfer assays of the indicated proteins (right).
(F) The ubiquitin thioester (Ub(t)) was docked onto the FCCH domain of the Uba1-Ubc4 (left) and Uba1-Ubc15 (center) structures based on contacts observed in the ‘doubly loaded’ Uba1 structure (PDB: 4NNJ). Ub(t) was docked onto Ubc15 from the Uba1-Ubc15 structure based on the hUbcH5~Ub thioester intermediate mimic (PDB: 5FER), (right). The E2 residue on hC that was mutated to probe potential contacts between Ub(t) and E2 during thioester transfer is shown as red sticks.
(G) E1-E2 thioester transfer assays of the indicated proteins.
See also Figure S2.