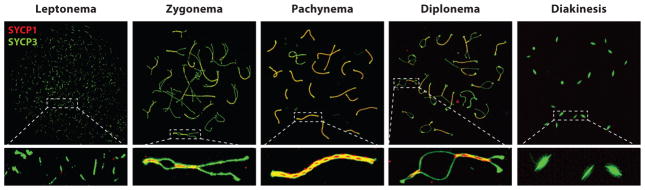
Figure 3.
Synaptonemal complex (SC) formation and synapsis during prophase I in mouse. Meiotic chromosome spread preparations from male mouse spermatocytes are immunofluorescently stained and imaged at different stages of prophase I using 3D structured illumination microscopy (3D-SIM). During prophase I, axial elements [stained with antibodies against SYCP3 (green)] start to form along the homologous chromosomes during leptonema. In zygonema, axial elements have formed along the entire axis of the homologous chromosome, and as synapsis occurs proteins of the central/transverse filament [stained with antibodies against SYCP1 (red)] begin to zipper the homologous chromosomes together. In pachynema, full synapsis has occurred along all autosomes and within the pseudoautosomal region of the sex chromosomes (in males). During diplonema, the SC starts to disassemble and homologous chromosomes repel each other, except for at regions of crossovers. Finally, at diakinesis, the axial elements are visible only at the centromeres.