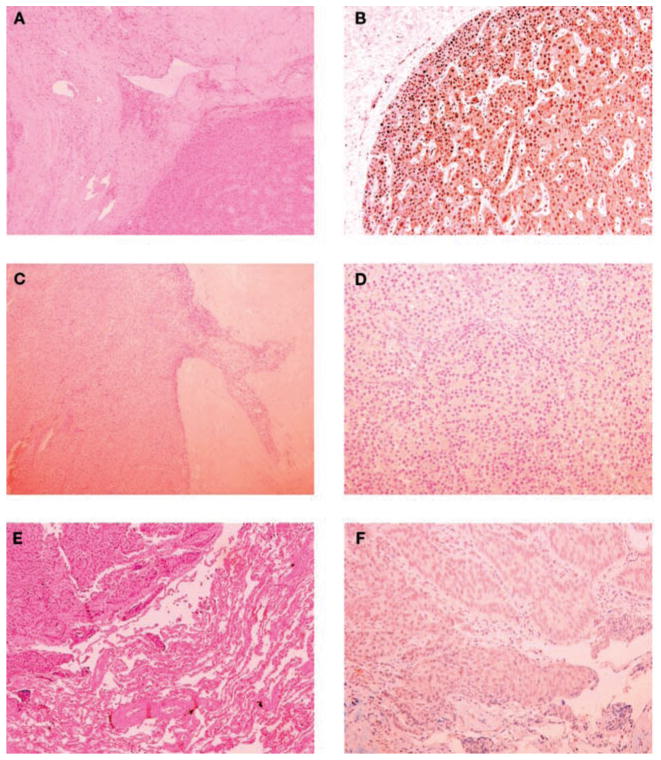
Fig. 1.
Pathology (left panels) and parafibromin immunohistochemistry (right panels) of the parathyroid tumors and lung metastasis. Upper panels: Parathyroid tumor of patient #1. A) Trabecular pattern with fibrous vascular pseudo invasion (hematoxylin and eosin, ×100); B) diffuse nuclear immunoreactivity of parathyroid cells (×200). Middle panels: Parathyroid tumor of patient #2. C) Oncocytic cells arranged in trabeculae, fibrous bands, and capsular invasion (hematoxylin and eosin, x100); D) the neoplastic cells were completely negative for parafibromin (×200). Lower panels: Lung metastasis of patient #2. E) A solid trabecular neoplastic lesion and adjacent normal lung parenchyma (hematoxylin and eosin, ×100); F) the tumor cells showed a diffuse loss of parafibromin staining (×200).