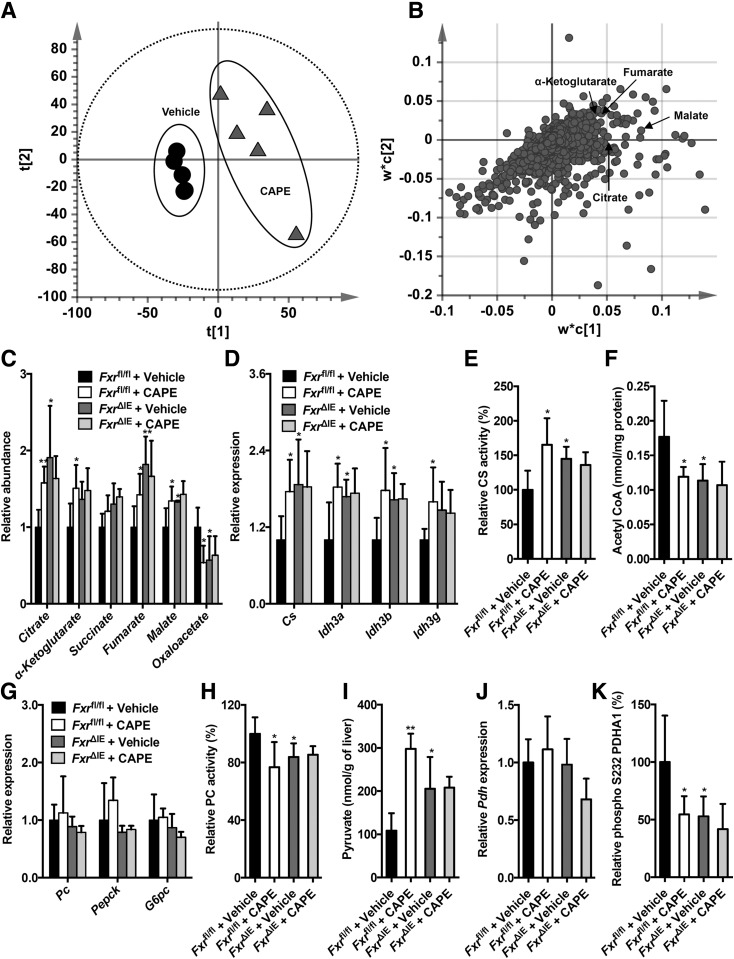
Figure 2.
CAPE decreases hepatic mitochondrial acetyl-CoA and inhibits PC activities dependent on intestine FXR. Score scatter plot of a PLS-DA model of the liver ions (A) and loading scatter plot of a PLS-DA model of the liver ions (B). C57BL/6N mice on an HFD were orally treated with or without CAPE for 4 weeks (n = 5). C: The relative levels of TCA cycle–related metabolites. D: Quantitative PCR (qPCR) analysis of the hepatic expression of mRNAs encoded by the TCA cycle–related genes. E: The mitochondrial CS activities in the liver. F: The mitochondrial acetyl-CoA levels in the liver. G: The mRNA levels of the hepatic gluconeogenic genes. H: The mitochondrial PC activities in the liver. I: Pyruvate levels in the liver. J: qPCR analysis of the hepatic Pdh mRNA levels. K: The hepatic phospho-PDH activities. C–K: Fxrfl/fl mice and Fxr∆IE mice on an HFD were orally treated with or without CAPE for 4 weeks (n = 5). Data are presented as the means ± SD. One-way ANOVA with Tukey correction: *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 vs. vehicle-treated Fxrfl/fl mice.