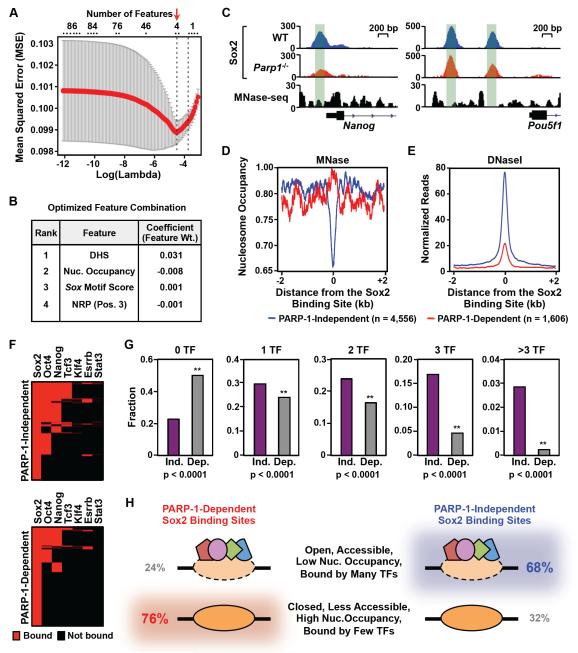
Figure 4. Genomic determinants of PARP-1-dependent Sox2 binding.
A) Identification of a minimal set of genomic features that accurately predict the PARP-1 dependence of Sox2 binding sites using the machine learning algorithm, LASSO (Tibshirani, 1996). The features included nucleosome occupancy, transcription factor co-occupancy, DNaseseq signal strength, Sox motif sequence, rotational orientation of the Sox motif in the nucleosome, and predicted structural features of the DNA at Sox2 binding sites (e.g., nucleosome rotational positioning, minor groove width, roll, x-displacement, slide). Prediction accuracy was evaluated by 10-fold cross validation. The combination of features that produced the best prediction accuracy with the smallest mean squared error (MSE; Y-axis) was selected (red arrow). X-axis, Log10 values of the penalty score lambda. Top, Number of features corresponding to the respective lambda values.
B) List of the optimized feature combination from the LASSO algorithm producing the best prediction accuracy. The complete list of 86 features tested in this analysis is listed in the Supplemental Materials.
C) Genome browser tracks of Sox2 ChIP-seq data and MNase-seq data around the Nanog gene in WT and Parp1−/− mESCs. The green shading highlights the relationship between Sox2 binding and nucleosome occupancy.
D) Average MNase-seq signals surrounding PARP-1-dependent (red) and PARP-1-independent (blue) Sox2 binding sites in mES cells. The data are centered on the Sox2 binding sites determined by ChIP-seq (± 2 kb).
E) Average DNase-seq signals surrounding PARP-1-dependent (red) and PARP-1-independent (blue) Sox2 binding sites in mES cells. The data are centered on the Sox2 binding sites determined by ChIP-seq (± 2 kb).
F) Heatmaps showing the binding of other transcription factors at Sox2 binding sites. Top, Results for PARP-1-independent Sox2 binding sites. Bottom, Results for PARP-1-dependent Sox2 binding sites. Red, significant binding. Black, no significant binding.
G) Fraction of PARP-1-independent (Ind.) and PARP-1-dependent (Dep.) Sox2 binding sites associated with the specified number transcription factors (TFs; 0, 1, 2, 3, >3) based on ChIP-seq in mESCs. Asterisks indicate significant differences (Fisher’s exact test, p-value < 0.0001).
H) Summary of genomic features for PARP-1-independent and PARP-1-dependent Sox2 binding sites based on Fig. 4 and Fig. S4. 76% of PARP-1-dependent Sox2 binding sites have the features shown in the bottom row, while 68% of PARP-1-independent Sox2 binding sites have the features shown in the top row.
See also Fig. S4.