Figure 2. Role of cardiolipins in homeostasis.
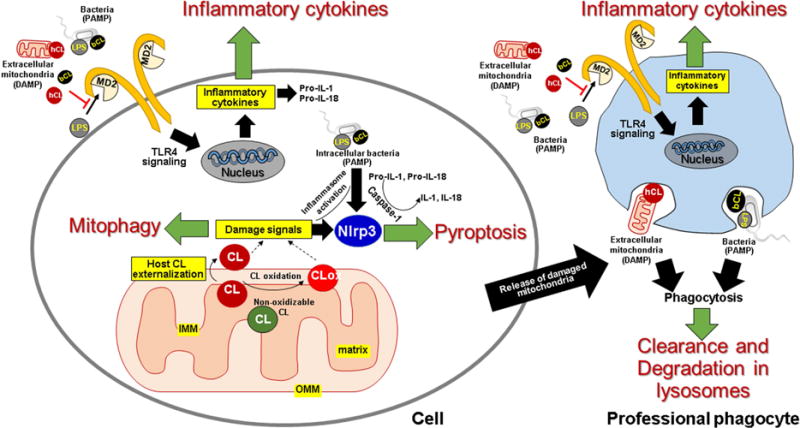
Intra- or extracellular signaling by CL is triggered by its externalization to the mitochondrial surface. Intracellular CL: In healthy cells, CL is exclusively localized in the inner mitochondrial membrane (IMM) specifically on the inner leaflet of the IMM that faces the matrix. Damage to the mitochondria results in loss of this asymmetry and movement of the lipid to the outer leaflet of the IMM, to the inner leaflet of the outer mitochondrial membrane (OMM), and finally to the outer leaflet of the OMM. Additionally, oxidative stress results in peroxidation of oxidizable CL (having polyunsaturaed acyl chains) by cytochrome c, to produce CLox, which may also be presented at the mitochondrial surface as a damage signal. Once at the mitochondrial surface, CL in the presence of cytoplasmic LC3, signals clearance of the damaged organelle by mitophagy, thereby restoring intracellular homeostasis. Under pathological conditions, such as presence of intracellular pathogens or presence of intracellular pathogen associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) like lipopolysaccharide (LPS), mitochondrial CL and/or CLox promotes activation of the NLRP3 dependent inflammasome pathway that directs cell death by pyroptosis. Extracellular CL: Mitochondria released following cell damage provide human CL (hCL) as a source of extracellular damage associated molecular patterns (DAMPs), which challenge host cells, including professional phagocytes. Similarly, infections challenge these cells with bacterial CL (bCL) and LPS. Both hCL and bCL signal engulfment of mitochondrial and bacterial membranes by professional phagocytes for subsequent degradation in lysosomes. hCL and bCL also interfere with binding of LPS to MD2, thereby attenuating Toll-like receptor (TLR)-4 dependent inflammatory cytokine production. The attenuation of cytokine response and phagocytic clearance both contribute to restoration of homeostasis.
