Fig 5.
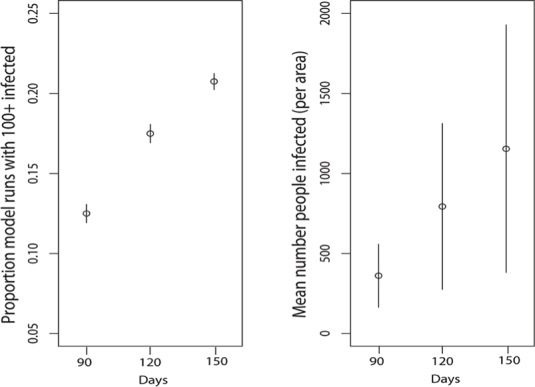
Season length (days, x axes) is positively associated with a) the proportion of model runs that resulted in 100 or more human infections with chikungunya virus and b) potential mean numbers of infected humans per square mile. Significant human infection is possible at even 90 days and uncertainty shown captures variability across cities, as well as human biting propensity and other parameter states. The mean number of people infected moves from 396 to 892 to 1376 and the median from 2.1 to 2.4 to 2.5 as season increases from 90 to 150 days.
