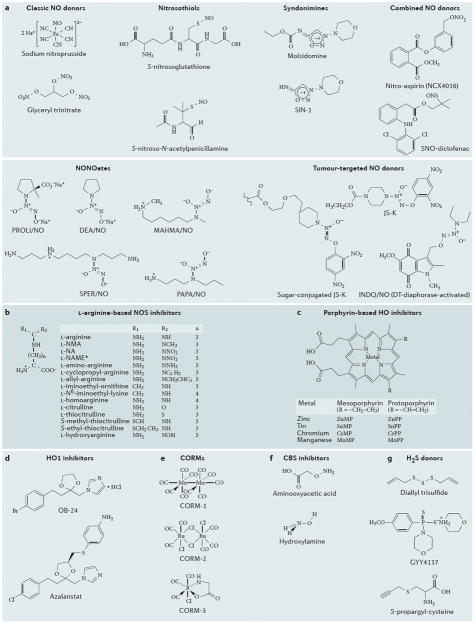
Figure 2. Chemical structures of selected compounds that affect levels of gasotransmitters.
a | Chemical structures of selected NO donor molecules. SNP and glyceryl trinitrate are considered “classic molecules”, which have been used by cardiologists for several decades. Nitrosothiols, syndonimines and NONOates have different half-lives/NO release profiles, but do not offer tumor-cell selectivity. The examples indicated in the figure are research compounds, rather than clinical development candidates. The “combined NO donors” (selected examples of which are shown here) offer the combined pharmacological action of the parent compound (e.g. a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory) and the NO donating group; several members of this class are in various stages or preclinical or clinical development. The tumour-targeted NO donors utilise specific features of the tumour microenvironment to direct the release of NO within the tumour cells, in order to increase tumour cell specificity and to reduce potential systemic side effects of NO; these compounds are currently in preclinical testing. b | Chemical structures of selected L-arginine-based NOS inhibitors. In L-NAME, the acid functional group (-COO–) becomes CO-O-CH3; **GW273629 is (3-[[2-[(1-iminoethyl)amino]ethyl]sulfonyl]-L-alanine); the central portion of the molecule contains a sulfonyl group within a 3-membered carbon chain; cindunistat is S-[2-(ethanimidoylamino)ethyl]-2-methyl- L-cysteine, where the central portion of the molecule contains a sulfur atom within a 3-membered carbon chain. c | Chemical structures of porphyrin-based haem oxygenase 1 (HO1) inhibitor compounds. Zinc, tin, manganese and chromium protoporphyrins have been described as competitive inhibitors for HO1 in the liver, spleen, kidney and other tissues. Most studies in cancer utilize ZnPP and SnPP. Sn-mesoporphyrin (Stanate; InfaCare Pharmaceutical Corporation) is noteworthy, as it has already been used in human studies. d | Chemical structures of selected non-porphyrin-based HO1 inhibitor compounds. OB24, an imidazole-dioxolane compound, is a member of a large group of compounds (that also contains imidazole ketones and imidazole alcohols) that are competitive inhibitors of HO1. OB24 has demonstrated efficacy in tumour-bearing mice models in vivo. Azalanstat is another potent HO1 inhibitor (IC50 values: 6 and 28 μM for rat HO1 and HO2, respectively). e | Chemical structures of selected CO-releasing molecules (CORMs). Each CORM molecule releases 1 molecule of CO; CORM1 and CORM2 releases CO rapidly (half-life: approx. 1 minute); CORM3 is a slower releaser of CO (half-life: approx. 1 hour). f | Chemical structures of two inhibitors of the hydrogen sulfide-producing enzyme cystathionine-β-synthase (CBS). G. Chemical structures of commonly used H2S donors.