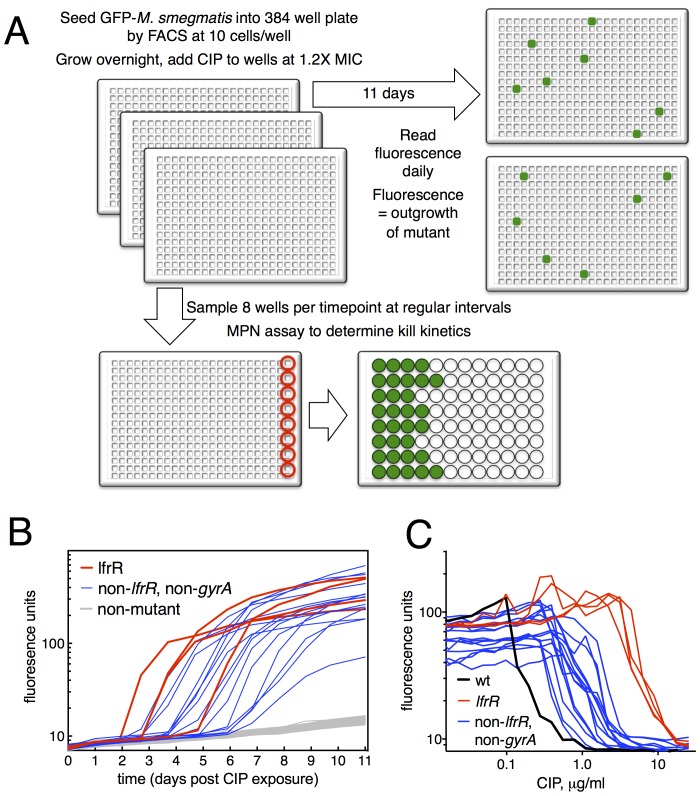
Figure 1. Selection of mutants at low ciprofloxacin concentration in 384 well plates.
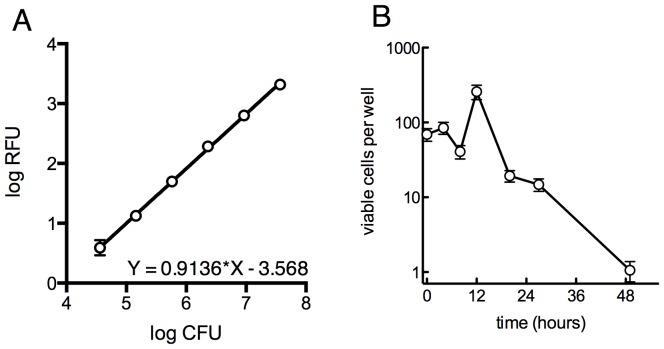
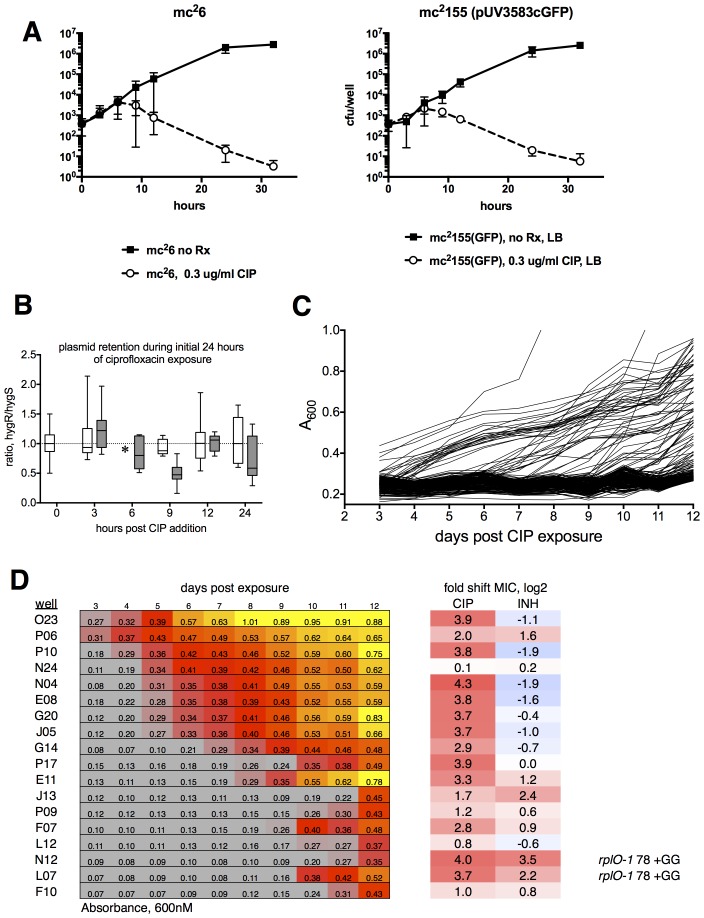
(A) Schematic of the selection strategy. Starting at t = −16 hr, 10 M. smegmatis cells are introduced into wells of three 384 well microtiter plates containing 15 µl of growth medium and grown overnight at 37°C. At t = 0, 15 µl of medium containing CIP are added to yield a final CIP concentration of 0.3 µg/ml. Plates were sealed with foil and placed at 37°C. At t = 0 and at roughly daily intervals afterwards, plates 1 and 2 were read in a fluorimeter (485 ex., 538 em., 530 cutoff). Plate three was used to monitor bacterial survival; at regular intervals, the foil seal was cut and peeled to expose a subset of 8 wells that were harvested using a robotic pipettor and serially diluted (10-fold). Growth of serial dilutions was measured after one week and the bacterial population at the time of harvest was then calculated using most-probable number method. Frequency of resistant mutants is calculated by the equation:. (B) Emergence of mutants in 0.3 μg/ml CIP. Outgrowth was detected by fluorescence (y-axis). Each line represents a single well followed over time (x-axis). (C) CIP sensitivity of wild-type M. smegmatis (black) compared with lfrR mutants (red) and non-lfrR, non-gyrA mutants (blue). Each line represents a unique mutant and illustrates outgrowth as measured by fluorescence (y-axis) as a function of CIP concentration (x-axis). Data are the average of duplicate wells.