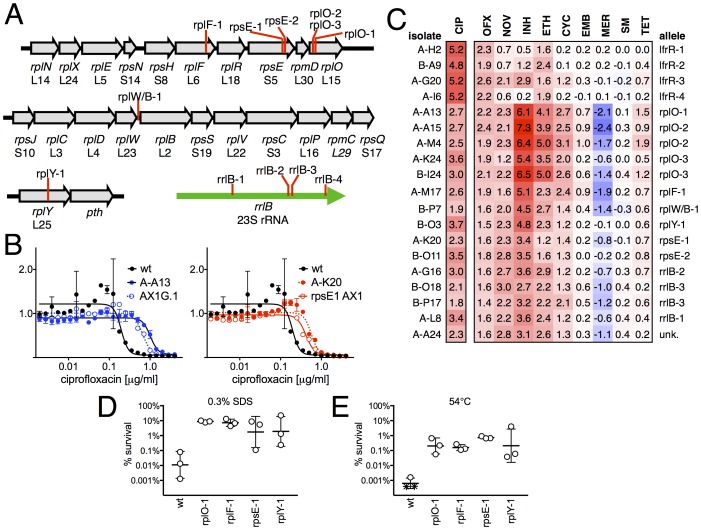
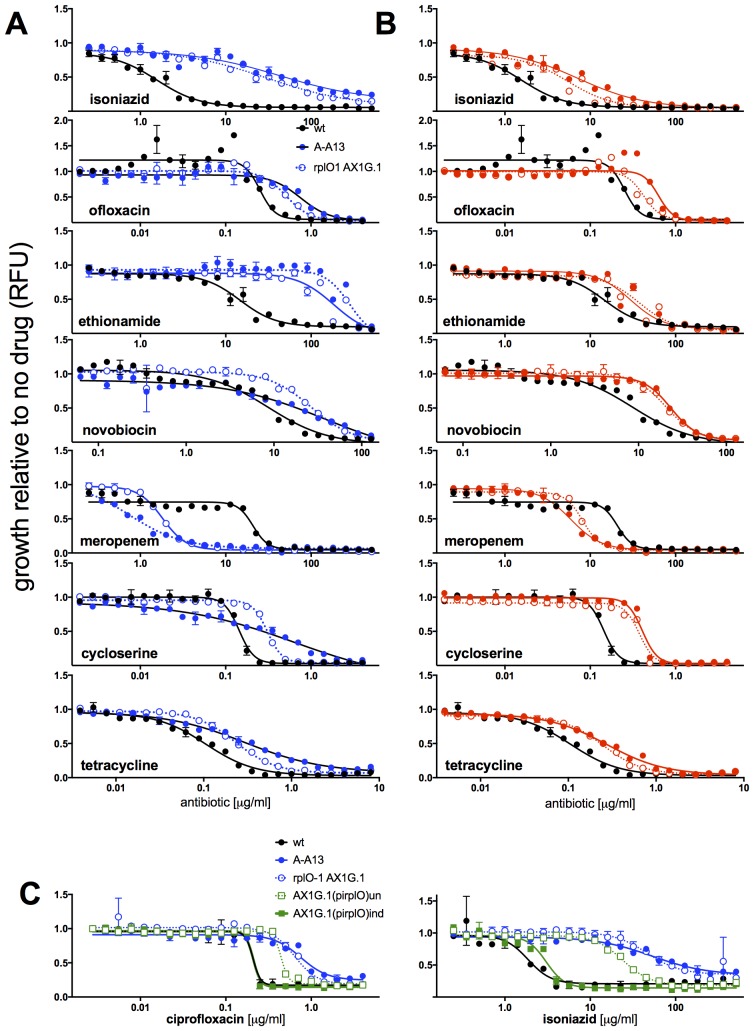
Figure 2. Ribosomal mutants are resistant to multiple antibiotics and environmental stressors.
(A) Schematic of the four regions of the M. smegmatis chromosome in which mutations in ribosomal components were found. Detailed descriptions of the mutations are provided in Table 1. (B) Introduction of the rplO-1 or rpsE-1 allele via homologous recombination (yielding AX1G.1 and rpsE1 AX1, respectively) confirms these mutations confer ciprofloxacin resistance. All strains carry pUV3583c and express GFP. Fluorescence of wild-type, mutant, and allelic-exchange derived strains was measured after 2 days of antibiotic exposure. Y axis is GFP signal normalized to untreated controls, x-axis = 1.41 fold (√2) dilution series of antibiotic, data are average of duplicate wells. (C) Numbers and shading show the IC50 shift (log2 transformed) of 19 mutants to a panel of antibiotics. Red = resistance, blue = sensitivity. OFX = ofloxacin, NOV = novobiocin, INH = isoniazid, ETH = ethionamide, CYC = cycloserine, EMB = ethambutol, MER = meropenem, SM = streptomycin, TET = tetracycline. (D) Bacteria were exposed to 0.3% SDS for 1 hr, and survival was measured by plating for colony forming units.. Dots represent individual biological replicates, each assayed in duplicate. * indicates < level of detection (approximately 0.0005%). For all mutants tested, <0.05 relative to wt (student’s T-test, survival data log transformed). Lines represent mean ± SE. For rpsE-1, p=0.054 relative to wt (student’s T-test, survival data log transformed), all others p<0.05. (E) Bacteria were incubated at 54°C for 2 hr. Data represented and analyzed as in (C).